Amino acids are important substances that are necessary for the development of the body, the normal functioning of all organs. With their shortage, serious health problems can occur. Because it is so important to know what foods contain amino acids, and fill their shortages.
What are proteins and amino acids for?
The human body is 20% protein. It is necessary for the work of the whole body. Amino acid is a component of protein, an organic compound that is needed to build a cell structure.
Without amino acids, the process of delivering nutrients to organs and tissues is impossible. Amino acids need a person to:
- positive mood;
- production of protein and its enzymes;
- concentration of attention;
- sexual activity;
- recovery of muscle and tissue fibers;
- beautiful skin and hair;
- full sleep.
Any disease leads to an imbalance of essential substances in the body. Amino acids are just responsible for their entry into the body. When protein is consumed, they break down inside the digestive tract into individual amino acids, from which proteins, hormones, and digestive enzymes are synthesized. This complex process is called protein biosynthesis. The body should regularly receive various amino acids from food, dietary supplements and through its own production, that is, biosynthesis.
The value of amino acids in the body
With a lack of amino acids, protein production slows down, metabolic processes begin to disrupt, the rate of elimination of toxins and decomposition products is significantly reduced. And older people are not the only ones who can suffer from it. Young people also feel the lack of nutrients. With an insufficient amount of amino acids in the body, such signs may appear as:
 weight problems;
weight problems;- decreased libido;
- arthritis;
- diabetes;
- poor skin condition;
- hair deterioration: brittleness, dryness;
- severe mood swings;
- sleep problems;
- hypertension, etc.
Benefits and uses of amino acids
For athletes
Amino acids are an integral part of our body and all processes that occur in it. Maintaining a balance of amino acids through the use of dietary supplements is beneficial for the body. This will stimulate muscle growth, improve the immune system. The greatest benefit of supplements with amino acids is their ability to repair muscles, prevent muscle fatigue.
Isoleucine, aspragin, glutamine, aspartic acid, and leucine are amino acids that are metabolized in muscles during dormancy. They also play a major role in the production of protein, the formation of energy.
During the first 15 minutes of exercise in the body, there is a reaction involving alanine aminotransferase. The main goal is to maintain a high level of certain amino acids during training. But the intermediate compounds that appear as a result of this reaction can cause fatigue. However, glutamine also performs other functions in the body that allow it to be used as a source of nutrition. It is for this reason that glutamine supplements increase muscle energy, the level of muscle metabolism during exercise.
Such beneficial properties make dietary supplements based on these amino acids ideal not only for professional athletes, but also for those who lead a healthy lifestyle. An experiment was conducted 20 years ago to determine the reactions of muscle protein to amino acid intake.
 Six women and men consumed the drink, which consisted of 5 g of essential amino acids, others took a placebo drink (pacifier) one hour after workouts. Those who took amino acids, increased the level of phenylalanine, which was not the case with those who took the pacifier. This increase led to an anabolic response in the muscles. Scientists have concluded that amino acids stimulate protein anabolism and muscle protein synthesis.
Six women and men consumed the drink, which consisted of 5 g of essential amino acids, others took a placebo drink (pacifier) one hour after workouts. Those who took amino acids, increased the level of phenylalanine, which was not the case with those who took the pacifier. This increase led to an anabolic response in the muscles. Scientists have concluded that amino acids stimulate protein anabolism and muscle protein synthesis.
In addition, in 2003, in one of the scientific reviews, it was stated that an increase in the concentration of lecithin protein in the body can stimulate the synthesis of muscle protein in the catholic state, which is caused by diets or tedious workouts.
Slimming
Amino acids are useful not only to those who want to build muscle and speed up their recovery. They are shown to apply and those who wish to lose weight. In one study, two groups of people who wanted to lose weight were observed.
The first group "sat" on a diet high in amino acids, the second - with a low one. Two weeks later, scientists found that those people who took more amino acids lost more fat and less muscle mass than the second group.
Thus, it can be said that a diet with an increased level of protein and amino acids, as well as with a low carbohydrate content will provide greater fat loss, while the body will maintain protein.
With diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which insulin is produced in the body. Consumption of carbohydrates increases glucose levels. With diabetes, our body cannot properly produce insulin to return sugar levels to normal, which can cause hyperglycemia. Amino acids have a positive effect on blood sugar levels. For example, arginine improves the transfer of substances that have a direct effect on insulin sensitivity.
With arthritis
Another useful property of amino acids is a decrease in the activity of inflammatory processes. In a study conducted in 1973, scientists proved that amino acid esters and sulfur-containing amino acids, for example, methionine and cysteine, are effective anti-inflammatory agents that reduce the effects of edema, anaphylactic shock, reduce inflammation, improve arthritis.
For the immune system
Few people know, but the lack of food protein and amino acids can cause a weakening of the immune system. As a result, the body's susceptibility to disease increases. In particular, recent studies prove that arginine, cysteine, glutamine play an important role in the work of our defense system. For example, these amino acids are involved in the activation of various lymphocytes, that is, killer cells, macrophages - they interfere with the work of cellular functions, affect the production of antibodies and other toxic substances. Modern scientists have come to the conclusion that dietary supplements, which contain amino acids in their composition, improve the immune system, reduce morbidity and mortality.
For fertility
Recent studies have shown that amino acid supplements increase fertility. For example, in one study involved more than 130 men with impaired fertility. For 90 days, they took dietary supplements with amino acids and microelements. The control group consisted of a group of 70 males with reduced fertility who took amino acids. All the results of the study proved a significant improvement in the conception area compared with the control group. Within six months after the completion of the experiment, a group of men who took supplements with amino acids recorded 34 cases of conception.
How to take amino acids in the form of dietary supplements?
An important rule in their use - compliance with the rules. You must also take into account the form of release of the drug, the purpose of the reception.
Slimming
In order to achieve the desired effect from fat burning workouts, it is necessary to take amino acids about 3-4 times a day in the morning and at night - these are mandatory rules. The exact dosage depends on the parameters of the body, the amount and quality of training.
Rules for taking pills or capsules:
- 3-5 - before training;
- no more than 3 tablets between meals;
- take 3-5 times a day;
- half an hour before a workout and 20 minutes after it (at least half an hour before bedtime).
Amino acids should be washed down with clean water.
Liquid:
- recommended dosage - 3 g;
- The number of admissions per day is 5 times.
In powder form:
- take 20 minutes before meals before workouts, after class and before bedtime;
- only water can be used for breeding;
- dosage per serving - 10 g.
For muscle growth
To build muscle, you need to take amino acids before and after exercise, and during the "drying" period they will help suppress the feeling of hunger.
In capsules or tablets:
- 20 minutes before and after workouts;
- you can drink water or kefir;
- take at least 4 times a day.

Liquid:
- dosage - about 5 g per serving;
- take at least 5 times a day.
Powder:
- take 20 minutes before and after workouts, before bedtime;
- for dilution of powder, you can use juice, water, milk;
- The dosage for 1 serving is about 10 g.
Also, do not neglect the instructions of the manufacturers, which are indicated on the packaging.
Amino Acid for Women
Amino acids help women not only to lose weight, but also to normalize the production of hormones that affect the condition of the skin, nails and hair. With insufficient intake of these substances, the woman begins to experience excessive irritability.
Wrinkles, acne may also appear, hair becomes brittle, skin loses its elasticity and becomes flabby. With a strong lack of amino acids increases the risk of having a baby with diseases. Therefore, to monitor their entry into the body of a woman is very important during pregnancy.
Women especially need amino acids such as:
- Tyrosine is responsible for burning fat while accelerating metabolic processes.
- Leucine. Controls calorie consumption during weight loss.
Essential and replaceable amino acids for humans: a list
Essential Amino Acids
These include:
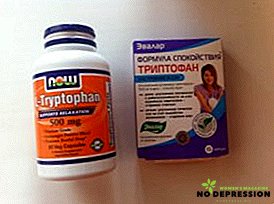 Leucine. Helps reduce blood sugar levels, slows down the destruction of tissues, removes extra pounds, promotes muscle regeneration, increases the secretion of growth hormone, reduces the number of leukocytes.
Leucine. Helps reduce blood sugar levels, slows down the destruction of tissues, removes extra pounds, promotes muscle regeneration, increases the secretion of growth hormone, reduces the number of leukocytes.- Lysine. Fights viruses, especially herpes and respiratory infections. Assists in the creation of antibodies of collagen, strengthens the immune system. Helps in the development of muscle protein, growth hormones, facilitates the absorption of calcium. Thanks to lysine, you can strengthen bones, make hair and nails more healthy, and increase libido. In combination with ascorbic acid, it can prevent vascular and heart diseases.
- Valin. The source of energy helps faster tissue repair. It is necessary for the correct work of the brain, the production of serotonin, it can also lower the sensitivity to cold or hot temperatures. It has a positive effect in the treatment of atherosclerosis.
- Tryptophan. An excellent helper in poor sleep, depression, depressed state. Regulates appetite, reduces the level of harmful cholesterol, synthesizes growth hormones, dilates blood vessels.
- Phenylalanine. Helps with the treatment of neurological diseases, depression. Increases the overall emotional background, improves the pancreas and liver. It has a positive impact on mental work, on the processes of memorization, the ability to concentrate, increases the production of thyroid hormones.
- Isoleucine. An essential amino acid for athletes: increases stamina, accelerates muscle recovery processes.
- Methionine. Essential for digestion, elimination of toxins. Also needed for the synthesis of creatine, which increases endurance and helps with allergies. Methionine improves the condition of diseases of the joints, supports the beauty and health of hair. In the absence of this amino acid can not talk about healthy bones, especially it is necessary for children. Participates in the production of elastin, collagen, is involved in the work of many systems and organs.
- Arginine. It is needed during the growth of the body, in diseases, in old age, because during this period the body cannot produce this amino acid on its own. Rejuvenates the body, increases the production of growth hormones.
- Histidine. Necessary for the process of blood formation, the formation of hemoglobin. It produces gastric juice, increases libido, prevents the appearance of allergic and autoimmune reactions.
Replaceable amino acids
Synthesis of replaceable amino acids occurs in the body, but many athletes or those who lead an active lifestyle, additionally use protein drugs. With constant physical activity, it is necessary to replenish the amount of replaceable acids, this will eliminate the feeling of fatigue, build muscle mass. Replaceable amino acids include:
- Alanine Participates in the production of carbohydrates, normalizes glucose levels, adds energy.
- Arginine. Strengthens immune forces, optimizes nitrogen balance.
- Asparagine It supports the work of the nervous system, prevents excessive arousal, increases efficiency.
- Aspartic acid. Allows you to get rid of fatigue, activates the production of antibodies.
- Glutamine. It improves memory, helps to concentrate, fills the energy deficit.
- Glycine. Regenerates damaged tissue, reduces the risk of epileptic seizures.
- Proline Necessary for the formation of connective tissue.
- Serine activates the metabolism of fats and strengthens the body's defenses.
- Taurine is the basis of bile, is responsible for the breakdown of fats and maintains optimal cholesterol levels.
- Cystine activates all oxidative processes.
Signs of lack of amino acids
The first signs of protein deficiency are depression, fatigue, inability to concentrate. If the amount of protein drops catastrophically further, the following symptoms may occur:
- Drowsiness, problems with coordination, weakness, trembling in muscles. A person cannot do his work, because any movement causes pain in the muscles.
- Disturbed sleep, constant headaches. With an insufficient amount of hormones, it is difficult for a person to fall asleep, and the brain can feel a lack of oxygen, which leads to headaches.
- The appearance of rash, pallor of the skin. Lack of protein can lead to problems in the work of metabolic processes. The skin turns pale, covered with inflammations that are not treated by conventional methods.
- Mood changes. Because of this, a nervous breakdown can occur, and a previously calm person without a reason may begin to show aggression, to become alarming.
- Brittle hair and nail plates. Nails and hair, like other organs and tissues in the body, need a building material, so for their good condition, you need protein. In case of lack of hair, hair starts to fall out, dandruff can appear, white stripes form on the nails.
- Cuts and wounds do not heal for a long time. To build new cells, the body needs protein. With its deficiency, damaged surfaces slowly recover.
- Edema. In case of violation of the protein balance in the subcutaneous tissue, accumulation of excess fluid begins.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. This may indicate a difficulty breathing, pain in the heart, cough.
Amino acids: daily requirement, content in products
| Amino acid | Daily rate | Which products contain |
| Alanine | The daily rate of alanine is 3 grams for adults and up to 2.5 grams for children of school age. Excess doses may lead to chronic fatigue syndrome. | Meat, seafood, egg whites, milk and dairy products, oats, wheat, beans, avocados, nuts. |
| Arginine | The daily need for arginine in children is 4-5 g, while in adults - not more than 6 g. | Pumpkin seeds, chocolate, coconuts, cornmeal, beef, oats, sesame, whole-wheat flour, yogurt, liver. |
| Aspartic acid | 12.2 g | Dairy products, meat (beef), salmon, rye, wheat, cheese. |
| Valin | The average daily rate of valine is 3-4 g (40.2 mg according to WHO recommendations). | Mushrooms, meat, cereals and legumes, dairy products, soybeans, nuts, lettuce, chicken, dried rice. |
| Histidine | The average daily consumption of histidine is 12 mg per kilogram of weight. | Poultry meat, cheeses, bananas, tuna, salmon, pork (tenderloin), beef fillet, legumes, seeds. |
| Glycine | The daily rate of glycine is about 3-6 g (depending on the intensity of physical and mental stress). | Meat, animal liver, gelatin and its by-products, fish, chicken eggs, nuts, cottage cheese. |
| Glutamine | Drinking 5 g of a substance twice a day will significantly strengthen the immune system. Bodybuilders, whose goal is building muscle, can increase this dose by 2 times. | Meat, dairy products, cheeses and cottage cheese, beans, spinach, parsley. |
| Glutamic acid | 16 grams | Spinach, parsley, cabbage, legumes, beets, meat (beef and chicken), dairy and dairy products. |
| Isoleucine / Leucine | The daily intake of isoleucine is 3-4 g (35.4 mg). Leucine - 109.5 mg (according to WHO recommendations). |
|
| Lysine / hydroxylysine | An adult’s daily requirement for an amino acid is about 25 mg / kg or about 150 mg. | Potatoes, meat (especially pork), yogurt, nuts, soybeans, wheat germ, chocolate, egg white, lentils, fish, spinach. |
| Methionine | 110.4 mg | Мясо, яйца, семена, бобовые культуры, чеснок, лук, молоко и молочные продукты, печень трески, филе лосося, крупы, орехи, кукурузная и пшеничная мука. |
| Орнитин | 500 мг-2г | Мясо, рыба, яйца, молочные продукты. |
| Пролин/ гидрокси-пролин | 4,5 г | Мясо, рыба, молоко, яблоки. |
| Серин | 8,3 г | Молочные продукты. |
| Таурин | 400 мг | Креветки, крабы, моллюски, рыба (особенно печень), устрицы, мидии, раки, говядина. |
| Тирозин | 500-1500 мг (в зависимости от интенсивности физических и умственных нагрузок). | Арахис, бобовые культуры, мясо, рыба, пшеница, морепродукты, яйца, семечки, молочные продукты, миндаль, творог, авокадо, сыр. |
| Треонин | Суточная норма треонина составляет около 0,5 г для взрослого человека и около 3 г - для ребёнка. | Мясо, грибы, крупы, молочные продукты, яйца, кунжут, орехи, бобовые культуры, морепродукты, анчоусы. |
| Триптофан | 3,5 мг на один килограмм веса. | Бурый рис, домашний сыр, грибы, овес, бананы, соевые бобы, сушеные финики, кунжут, рыба (особенно тунец), кукуруза. |
| Фенилаланин | 30 mg | Говядина, курица, рыба, соя, орехи, яйца, творог, молоко, бобовые культуры, семечки. |
| Цистеин/ цистин | 1,8 г | Яйца, овес, кукуруза, мясо птицы, кисломолочные продукты, зародыши пшеницы, чеснок, лук. |
| Цитруллин | Максимальная эффективная суточная доза цитруллина составляет 6 грамм. | Арбуз, рыба, молоко, яйца, мясо, соевые бобы, арахис, лук, чеснок. |


 weight problems;
weight problems;
 Leucine. Helps reduce blood sugar levels, slows down the destruction of tissues, removes extra pounds, promotes muscle regeneration, increases the secretion of growth hormone, reduces the number of leukocytes.
Leucine. Helps reduce blood sugar levels, slows down the destruction of tissues, removes extra pounds, promotes muscle regeneration, increases the secretion of growth hormone, reduces the number of leukocytes.