Clinical tests that are prescribed by doctors during the examination are of great informative value. Based on them, it is realistic to identify many diseases. With regard to urine analysis, thus evaluated the work of the kidneys, metabolic processes in the body and much more.
To get a full result, it is important to properly prepare for the delivery of the analysis. Its true interpretation is important. Some deviations from the norm do not always indicate pathology; they may have many other reasons.
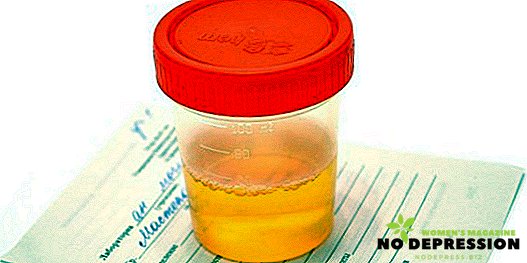
How to collect urine and pass the general analysis correctly
The accuracy of the result depends on how correctly the urine is collected. Otherwise, you will have to pass the analysis again. There is nothing difficult in this, so not only an adult, but also a child can perform the procedure. Based on this analysis, it is realistic to determine the following pathological conditions:
- acute and chronic kidney disease;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disease;
- benign or malignant tumors;
- infection in the urinary tract or in the body as a whole.

Doctors are usually prescribed to give a urine test to patients with certain indications. These should include:
- kidney and lower back pain;
- frequent urination;
- suspected diabetes;
- abdominal pain;
- pain when urinating, blood present;
- history of chronic diseases of the kidneys and bladder;
- the presence in the urine of foreign particles (crystals, flakes, etc.).
If the urine is not properly collected, the analysis will be unsuitable for diagnosis. In order to establish the disease, you will need many different diagnostic techniques. And this is only one of them, so it should not be considered the only accurate way to determine pathology.
Rules for collecting urine for research
- It is best to use a special container purchased at a pharmacy to collect and open it immediately before urination, then seal the lid tightly to prevent infection;
- If you use a regular glass jar, it must first be sterilized in boiling water for half an hour or 10 minutes in the presence of soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per cup of water);
- The container used must be thoroughly closed with a sterile cap;
- The jar should be dry;
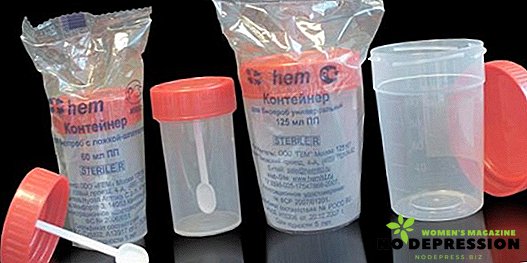
- It is imperative to thoroughly carry out hygiene of the genital organs, using soap or other antibacterial agents;
- The collection is carried out only in the morning and not in the evening or in the afternoon (just before taking the jar to the laboratory);
- First urinate into the toilet, and the medium portion is sent directly to the jar;
- If there is very little liquid in the container, the analysis will not be able to be carried out properly, therefore it is better to fill it by about two thirds;
- The jar should not be filled to the brim, so then urinate into the toilet.
It is not only important to correctly collect the liquid, but also to prepare the body for analysis. Experts give the following recommendations:
- you can not pass urine to women during menstruation, since red blood cells will be in it and the analysis will be completely uninformative;
- women need to remember that vaginal discharge can get into the jar, which also misinforms the laboratory technicians and it will be impossible to understand that leukocytes got from the urethra or the cervix (to avoid this, you need to make sure that there are no vaginal discharges);

- men also need to carry out hygiene of the genital organs, removing the foreskin and using antibacterial agents;
- the night before is not recommended to eat spicy and salty foods, as well as foods that are harmful to the kidneys;
- Drugs can greatly affect the result of laboratory tests, so they need to be excluded within a few days;
- antibiotics kill bacteria, their use even a week before the examination may affect the analyzes (it is better not to use them until the full picture is clear);
- if you drink a lot of water, the urine will be more diluted and transparent, and with a small amount of it - condensed and with a large sediment.
Urinalysis: the rate of indicators in adults
According to the amount of urine, its color, concentration, the presence of sediment and other characteristics determine certain pathologies (or rather, suggest with a basis for further examination - ultrasound, etc.).
 Normal urine should not have a dark color, be red or orange. Usually, when the kidneys work well, it is either transparent (if the person drinks a lot of water) or slightly yellow.
Normal urine should not have a dark color, be red or orange. Usually, when the kidneys work well, it is either transparent (if the person drinks a lot of water) or slightly yellow.
Should guard any deviations from the norm. A small amount of urine indicates edema, which is usually seen in pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and renal failure. It happens that the fluid gets too fast in the bladder.
In order to eliminate deviations from the norm, it is necessary to undergo an additional examination. Laboratory assistants evaluate the analysis on the following indicators:
- total amount of urine excreted;
- Colour;
- acid reaction;
- osmolarity (characteristic of concentration ability);
- density;
- the presence of protein (impaired kidney function);
- ketone bodies;
- sugar;
- the presence of acetone (indicates diabetes);
- red blood cells (blood);
- leukocytes (inflammatory process).
Deciphering indicators of urinalysis in adults: table
Some data that are recorded in the results of the tests are signs of pathology (although the final diagnosis is not made only on this basis, only an assumption).
Table of norms and deviations of urine analysis in adults (18 years and older)
| Total urine | 90-400 ml | less than 90 ml | • norm; • problems with heart; • dehydration; • chronic insufficiency (low density); • insufficiency of renal function. |
| more than 400 ml | • norm; • large volume of urination; • impaired renal function; • diabetes; | ||
| How clear is the urine | full | turbidity | • pyelonephritis; • presence of bacteria; • crystals. |
| impurities and flakes | • kidney disease; • the presence of bacteria and other infections; | ||
| Coloring | yellowish | red or orange | • the presence of bilirubin; |
| like meat slop | • kidney disease; • the moment when pebbles come out; • possible urogenital tuberculosis; • kidney oncology (suggestion). | ||
| brownish | • in the breakdown of amino acids | ||
| black shade | • warning sign (bleeding). | ||
| pronounced yellowish color | • possible after taking various drugs. | ||
| Colorless | • kidneys poorly concentrate urine; • too much fluid is consumed; • kidney disease; • use of diuretics; • poor kidney function. | ||
| pH | high acidity | neutrality | • presence of bacteria; • with vomiting; • when using medication; • poor nutrition. |
| alkaline reaction | • various infections; • after vomiting; • after special treatment; • food with a minimum amount of amino acids. | ||
| Osmolarity | 500-850 mmol / liter | Less than 600 mmol / liter | • loss of salt in different ways. |
| more than 800 mmol / liter | • presumed diabetes. | ||
| Urine specific gravity | 1,019-1,026 (1019-1026) | more than 1,026 (1026) | • norm; • sugar in the urine; • protein in the urine; • the presence of dehydration organism. |
| less than 1,019 (1019) | • fine; • kidney disease; • use of a diuretic; • large amount of water consumed; • poor kidney function. | ||
| Presence of acetone | _ | + | • diabetes. |
| Presence of protein | _ | + | Pus-provoking infection; injury: severe heart disease; kidney disease triggered by diabetes or hypertension; • neoplasms; • presence of glomerulonephritis; • possible pyelonephritis; • insufficiency of the heart and blood vessels; • impaired kidney function; • thromboembolic disease. |
| Sugar | _ | + | • an increased amount of glucose in the blood; • diabetes; • sick liver; • kidney inflammation; • poor renal system. |
| Ketone bodies | _ | + | • with diabetes. |
| The presence of leukocytes | for men: 0-3 in p / s, for women: 0-5 in p / s | 5-20 p / s | • possible pyelonephritis; • bacteria; • presence of glomerulonephritis; • kidney inflammation. |
| more than 20 p / s | • indicates pyelonephritis; • most often - cystitis; • usually urethritis; • prostatitis in the acute stage. | ||
| The presence of red blood cells | _ | less than 100 p / s | • serious kidney disease; • stones in the kidneys; • neoplasms; • bacteria. |
| more than 100 p / s | • stones in the kidneys; • impaired kidney function; • at a rupture of a renal cyst; • sepsis; • serious and dangerous renal dysfunction; • the presence of tumors, pyelonephritis or vasculitis. |
Physical indicators of urinalysis
The presence of certain additional inclusions, discoloration may indicate the beginning or progression of any pathological process. If a person took drugs, they can also affect the color and composition of urine.
Laboratory assistants evaluate first of all visually: color, presence of sediment, flakes, amount of urine. First, a specialist with secondary education checks, then re-checks by the laboratory doctor, who already finally indicates all the data obtained on the result sheet.

Even the negative aspects should not immediately frighten the patient, since many factors are influenced by many factors: the power on the eve of the test, the quantity and quality of the liquid consumed, the drugs taken.
If red blood cells, protein, bacteria are found in the urine without special reasons, this may indicate the presence of serious diseases. More research will be required.
In the case when the analysis would be delivered incorrectly, you need to retake it, especially when bacteria are detected. They could get into a jar in any way. But if a reanalysis reveals their presence, this indicates an inflammatory process in the kidneys.
Determination of organic matter in urine
The composition of urine mainly includes urea, which takes a large dose of such a liquid. It also contains a considerable amount of nitrogen. These substances are obtained by the body from food and excreted from the body as products of processing with urine.
Compared to urea nitrogen, about 85%. With an increase in the consumption of protein foods increases and its release. Such a condition is known in diabetes, high temperature, or in the process of tumor breakdown.

But the reduction of urea does not mean health. This may be the case when the patient is sick with hepatitis, hepatosis, glomerulonephritis.
Creatinine is another substance that is an indicator of pathology or its absence. Adults normally do not excrete it with urine. However, in patients with dystrophy or myopathy, this may occur.
 Protein in the urine (amino acids of various types) is observed in patients who have very serious pathologies. It can be injuries, severe infectious diseases, problems with the thyroid gland and even (in rare cases) oncological processes.
Protein in the urine (amino acids of various types) is observed in patients who have very serious pathologies. It can be injuries, severe infectious diseases, problems with the thyroid gland and even (in rare cases) oncological processes.
Depending on the food in the urine determine the amount of uric acid.
The more purine in food, the higher its concentration. Citric acid, lactic acid and oxalic acid, as well as some other substances, are released in the amount of up to one gram.
Examination of urinary sediment
The composition of urine sediment has important diagnostic value. It determines the number and presence of cylinders, red blood cells, white blood cells, salt crystals, epithelium. Blood should not be normal.
Red blood cells can appear in the smallest number - no more than 3 in sight. This takes place after severe physical overwork, illness.
If there are many red blood cells, it is about bleeding.
Leukocytes in men should not be more than 3 in sight, and in women and kids - no more than 6 in sight. Pyuria often indicates a serious inflammation of the kidneys, the presence of infection. In this case, bacteria are also most often detected.
A small number of cylindrical epithelium (renal tubular cells) is allowed. With a high amount of protein, the release of hyaline cylinders is observed. Patients with glomerulonephritis, diabetes, and other serious illnesses often have granular cylinders.
A very alarming phenomenon is waxy cylinders.

The number of epithelial cells in the normal to 10 in sight. Depending on the acidity, certain inorganic compounds can be detected in the urine. If the reaction is alkaline, find phosphates, amanium. When oxalic acid is abused, oxalates are detected, and in various serious diseases, uric acid appears in the form of large crystals.
If the urine test is not too positive, the doctor must prescribe additional treatment. It is important to note that each laboratory has its own indicators of the standard content of certain substances.
For more information on how to properly collect urine, see the following video.