Conjunctivitis (in some cases mistakenly written - conjunctivitis) is an inflammatory process on the conjunctiva (a thin film covering the visible part of the eye and the inner surface of the visible eyelids).
Conjunctivitis is one of the few diseases that has many sources and, accordingly, varieties. The disease is widespread among both children and adults. Children suffer from them through ignorance, and adults due to carelessness.

Types and causes of the disease
- Depending on the source of the disease, conjunctivitis is infectious and non-infectious.
- By the time and nature of the inflammation is divided into acute and chronic.
More about each:
- Chronic. Like any chronic disease, it bothers often and does not require special reasons for its occurrence. Inherent primarily in adults. The causes are long-term irritants (smoke, dust, chemical vapors and impurities). The disease is sluggish, the symptoms are subtle, is in the body for a long time. Chronic conjunctivitis has a common symptom for each attack.
- Acute. A single disease with a sharp jump in the amplitude of the course. Arises unexpectedly, immediately accompanied by pain, discomfort, secretions. The disease does not stay in the body for a long time, if the correct treatment is applied in time. Repeated illness with acute conjunctivitis is a completely new disease, with different symptoms and pathogens.
- Non-infectious. One of the manifestations of an allergic reaction, or occurs as a result of exposure to the eye of foreign objects (impact, sand, contact lenses, chemical drug, etc.).
- Infectious. Most often the root cause of acute conjunctivitis. Pathogens - microorganisms that enter the eye from the external environment or with blood flow.
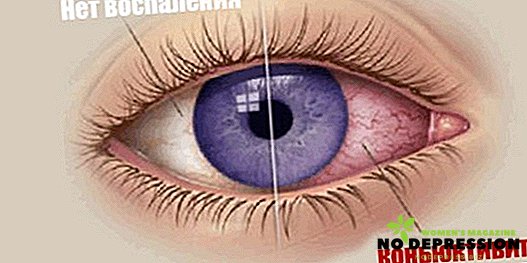
Infections in nature there is a mass. In the eyes, they fall most often due to dirty hands. It is not necessary to rub the eye with a hand stained in the ground. Suffice to say hello to the hand with the person, use a towel or pillow, or take up the handrail in public transport so that the infection is on your hands.
Which microorganisms cause inflammation of the conjunctiva:
- Bacteria. Most often - staphylococci and streptococci. Get into the eyes of the ponds. The habitat of these bacteria is stagnant water. Ponds, lakes and riverbeds located near cities are most often contaminated with bacteria. It is enough to dip your hands and touch their eyes, after a few hours, without first washing out what to say about swimming with your eyes open under water.

- Another representative of the cocci family is Neiser's gonococcus. An adult falls ill through the use of shared towels and bed linen with the patient or through his hands. More often one eye suffers inflammation, a severe general condition of the body and complications of the cornea are observed. Gonoblene is dangerous with consequences - due to severe swelling, there is a thorn in the eye, which leads to partial or complete loss of vision.
- Viruses. Viral conjunctivitis accompanies viral diseases or occurs when an adeno or ester virus is infected.
- Fungi. There are more than 50 types of fungi that can cause conjunctivitis. The most widely known is Candida. Organisms inhabit land, water and animals. A frequent source of the disease is an infected person. The transfer of fungi occurs through the use of shared towels with the patient, bedding, as well as upon contact with his insufficiently clean hands.
Conjunctivitis of the eye in adults: the first signs and symptoms
Depending on the source of the disease, conjunctivitis has various symptoms.
Bacterial:
- Severe redness of the mucous and ocular protein.
- Burning.
- Sensation of eye contamination.
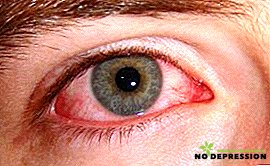
- Purulent discharge. Initially, they are watery, but after a few days they turn into a purulent form.
- Most often, both eyes are subject to inflammation.
- Severe eyelid edema.
Gonococcal conjunctivitis. Incubation lasts from 12 to 48 hours. Then the symptoms begin to appear:
- Severe eyelid edema.
- Purulent discharge.
- Hemoz.
- The body temperature rises.
- Joints and muscles are damaged. The patient feels pain and difficulty moving.
Viral conjunctivitis. Symptoms appear in parallel with the symptoms of ARVI and affect both eyes. Since the disease mainly enters the eye with blood flow, the time difference between the infection of the eyes is insignificant.
- The expansion of the eye vessels.
- Significant redness.
- Increases tearing.

- Itching sensation.
- Feeling of eye contamination.
- Serous discharge.
- Conjunctival follicle formation.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Rare manifestations - photophobia and corneal clouding.
Fungal conjunctivitis. Symptoms are mild, and the presence of a large number of varieties of fungi leads to a variety of symptoms and formations on the conjunctiva:
- Conjunctival edema.
- Purulent discharge.
- The presence of films on the conjunctiva.
- The duration of the disease.
- Greenish ulcers.
- Small nodules resembling grains.
- Papillary lesions.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in adults: drops
Depending on the cause of the occurrence, drugs of different composition and method of exposure are used.
Bacterial
Bacterial conjunctivitis is treated topically with a wide spectrum of antibiotics.
- Albucid (30%). Method of exposure to the drug - the cessation of reproduction of microorganisms. The main active ingredient is sulfacetamide. 30% solution contains 30 mg of active ingredient in 1 ml. Form release - vials of a solution of 5 and 10 ml. The dosage depends on the condition and is regulated by the ophthalmologist. In a critical condition, a maximum of 2-3 drops are prescribed 6 times a day.
 Has no pronounced contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Albucidum is not compatible with preparations containing silver salts. Simultaneous use of local anesthetics weakens the effect of the drug. Do not use in the presence of soft contact lenses - reduced transparency.
Has no pronounced contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Albucidum is not compatible with preparations containing silver salts. Simultaneous use of local anesthetics weakens the effect of the drug. Do not use in the presence of soft contact lenses - reduced transparency. - Levomitsetin. Method of exposure - inhibition of the synthesis of proteins of microorganisms. Wide spectrum antibiotic. The active ingredient is chloramphenicol (2.5 mg per 1 ml). release form - 10 ml vial. the duration of treatment is individual. Assign 1 drop of the drug 3 times a day, in both eyes. Side effects are extremely rare - itching, redness, tearing, irritation. The drug is contraindicated in patients with psoriasis, eczema, skin fungi, pregnant women, nursing mothers and children under 4 months. Affects driving. In case of overdose, reversible visual impairment is possible - you should immediately wash the eyes with a large volume of water. Pronounced drug interactions are not observed.
Viral
When viral conjunctivitis drugs are used local exposure, with the content of recombinant interferon or interferonogenov (stimulate the production of interferon).
 Ophthalmoferon. The composition includes interferon recombinant alpha - 2. Makes antimicrobial and antiviral effects. The release form - a bottle on 5 or 10 ml. Inherent effect of anesthesia, facilitating pain. It has no contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the composition of the drug. In the critical stage, 1-2 drops are prescribed up to 8 times a day. With an improvement in condition, the ophthalmologist can reduce the dosage up to 3 times a day. Side effects - a burning sensation in the first minutes after instillation. Individual sensitivity may cause an allergic reaction. Ophthalmoferon is not recommended for use with other drugs local effects.
Ophthalmoferon. The composition includes interferon recombinant alpha - 2. Makes antimicrobial and antiviral effects. The release form - a bottle on 5 or 10 ml. Inherent effect of anesthesia, facilitating pain. It has no contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the composition of the drug. In the critical stage, 1-2 drops are prescribed up to 8 times a day. With an improvement in condition, the ophthalmologist can reduce the dosage up to 3 times a day. Side effects - a burning sensation in the first minutes after instillation. Individual sensitivity may cause an allergic reaction. Ophthalmoferon is not recommended for use with other drugs local effects.- Poludan. Stimulates the production of interferon and has antiviral effects. For use as eye drops, 0.2 mg of the powder is dissolved in 2 ml of distilled water. The frequency of use - up to 8 times a day. Side effects and contraindications are not defined. Form release - 0.2 mg ampoule.
- Aktipol. Induces the production of interferon. Promotes regeneration and has an antioxidant effect, removes puffiness. Contraindications - individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Side effects are extremely rare - conjunctival redness. The simultaneous use of drugs based on sulfonamide (Albucid) and metabolic agents are not recommended. With a parallel intake of antibiotics, the effect of the antibiotic will increase. The release form - a bottle on 5 ml. The main active ingredient is aminobenzoic acid (0.07%). The frequency of use and dosage is prescribed individually by an ophthalmologist. As often as possible to use the drug can be 8 times a day.
Fungal
 Fungal conjunctivitis is treated with topical, antimycotic drugs. The preparations have different composition and conditions, allowing the use, due to a wide range of fungi species.
Fungal conjunctivitis is treated with topical, antimycotic drugs. The preparations have different composition and conditions, allowing the use, due to a wide range of fungi species.
- Amphotericin B. A highly specialized antifungal antibiotic. When applied topically, a variety of allergic reactions are possible. It has various side effects when using a variety of medical drugs.
- Levorin. Form release - powder for suspension. It is necessary to confirm the sensitivity of the fungus before starting treatment. Causes allergic reactions.
Methods of treating different types of conjunctivitis in adults
The method of treatment of conjunctivitis is as follows:
- Determining the source of the disease by observing and testing.
- The purpose of the drug is the active action of local application, which will make direct treatment, depending on the source.
- The appointment of hormonal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for internal use. The need for use depends on the severity of the condition.
- The use of local drugs that facilitate discomfort.
Allergic conjunctivitis requires the destruction of a source that causes allergies and the simultaneous taking of drops or ointments that relieve the sensation of itching, tearing and dryness.

Features of the treatment of acute and chronic conjunctivitis of the eye in adults
Acute conjunctivitis requires quick intervention and a pointed focus. The basis of the treatment of chronic conjunctivitis is the elimination of the cause of the disease.
If discharge is not abundant, use binders. In cases where chronic conjunctivitis becomes severe, methods of acute conjunctivitis are applied. Often herbal teas are used as the main treatment.
Treatment of folk remedies
Folk remedies are harsh and do not always bring a positive effect. The most innocent of all represented on the Internet - decoctions of herbs. Various sets of berries, their leaves, herbs and teas are used for washing the eyes.
You can do the "bath" - to the brim to fill a clean glass (cup) with broth, lower the face so that the eye is immersed in the liquid and blink them, opening the eyelid widely. During the procedure, the temperature of the broth should be warm!
Hot will burn, and cold will catch cold. More gentle way - compresses and washing. Compresses are simple - a small piece of gauze or a cotton pad is plentifully moistened in warm broth and applied to the eyes. The cooled compress is thoroughly washed and repeat the procedure.

Hips of elderberry, elderberry flowers, fruits of dill, raspberry leaves and flowers, as well as ordinary black tea are used.
Other methods, such as planting plant juices, using honey, fruits, vegetables and poultices, can lead to serious consequences. Until the loss of vision. If the compassionate neighbor advised "100% method!" better consult your doctor.
Preventive measures
Prevention is hygienic.
- Washing hands after the street.
- Do not touch your eyes with dirty hands.
- Do not open your eyes under water in ponds.
- Use individual bath and pastel accessories.
- Follow the rules for wearing contact lenses.
- Flush eyes with plenty of dust if dirt, dirt, dust, and chemicals get into them.
- Contact an ophthalmologist with the slightest symptoms or discomfort.
Attention to your body and timely assistance of a specialist will help to avoid severe forms of conjunctivitis and falling eyesight.
For more information about this disease, see the following video.






 Has no pronounced contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Albucidum is not compatible with preparations containing silver salts. Simultaneous use of local anesthetics weakens the effect of the drug. Do not use in the presence of soft contact lenses - reduced transparency.
Has no pronounced contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Albucidum is not compatible with preparations containing silver salts. Simultaneous use of local anesthetics weakens the effect of the drug. Do not use in the presence of soft contact lenses - reduced transparency. Ophthalmoferon. The composition includes interferon recombinant alpha - 2. Makes antimicrobial and antiviral effects. The release form - a bottle on 5 or 10 ml. Inherent effect of anesthesia, facilitating pain. It has no contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the composition of the drug. In the critical stage, 1-2 drops are prescribed up to 8 times a day. With an improvement in condition, the ophthalmologist can reduce the dosage up to 3 times a day. Side effects - a burning sensation in the first minutes after instillation. Individual sensitivity may cause an allergic reaction. Ophthalmoferon is not recommended for use with other drugs local effects.
Ophthalmoferon. The composition includes interferon recombinant alpha - 2. Makes antimicrobial and antiviral effects. The release form - a bottle on 5 or 10 ml. Inherent effect of anesthesia, facilitating pain. It has no contraindications, except for individual sensitivity to the composition of the drug. In the critical stage, 1-2 drops are prescribed up to 8 times a day. With an improvement in condition, the ophthalmologist can reduce the dosage up to 3 times a day. Side effects - a burning sensation in the first minutes after instillation. Individual sensitivity may cause an allergic reaction. Ophthalmoferon is not recommended for use with other drugs local effects.