Bladder catheterization is a medical procedure that is carried out either for treatment or for diagnostic purposes in diseases of the urogenital system. It is important that doctors comply with the algorithm of this procedure, it will avoid complications. For men and women, the technology of introducing a catheter will be different, due to the peculiarities of the structure of the urogenital system.
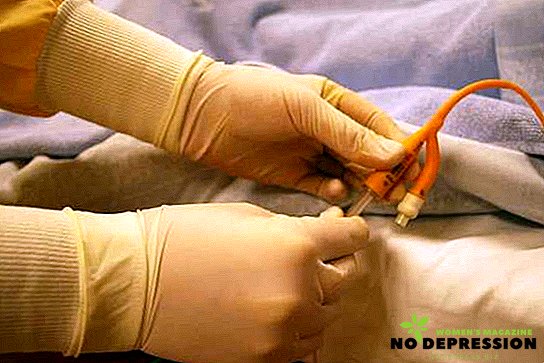
Purpose of catheterization
In some diseases of the urogenital system, for example, in a variety of pathologies of the kidneys, prostate adenoma, difficulties with urine excretion may be observed.
Bladder catheterization is a procedure in which a special device is inserted into the cavity of the urethra to remove excess fluid. Such manipulations require medical skills and knowledge from doctors, and can be carried out both as planned and as an emergency.
The main objectives of the procedure:
- medicinal;
- hygienic;
- diagnostic
If we talk about diagnostic purposes, this procedure helps to determine the cause of the pathology, since pure urine is the most reliable material for conducting tests. Catheterization, which is carried out with hygienic purposes, will provide the required care for a sick person who cannot empty himself.
 For therapeutic purposes, catheterization is carried out in the following cases:
For therapeutic purposes, catheterization is carried out in the following cases:
- for emergency removal of excess fluid in case of urinary retention for more than 10 hours (this can happen with diseases of the system);
- during the rehabilitation period after operations;
- in violation of urinary function.
Timely procedure to avoid deterioration of health.
What catheters are
The use of a catheter involves the introduction of a special tube with holes at the end directly into the urethra. Such devices can be both for short-term and for long-term use.
Catheters are:
- elastic;
- tough.
Rigid products are made of alloys of non-ferrous metals, they are quite traumatic - they are usually used only in the most severe cases.
For men and women, a variety of designs are used, and the introduction itself can be trusted only to an experienced specialist.
Elastic catheters are more convenient, and they are made of special rubber, silicone, soft plastic.
Drainage products are also:
- outdoor;
- internal or urethral.
 Each of these species has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, an external catheter is expelled through the abdominal wall, without affecting the urethra. It is easier to install, it is less traumatic. Moreover, when they are installed, a person will be able to have sex, which is important for long-term use.
Each of these species has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, an external catheter is expelled through the abdominal wall, without affecting the urethra. It is easier to install, it is less traumatic. Moreover, when they are installed, a person will be able to have sex, which is important for long-term use.
But internal catheters can damage the walls of the bladder with the introduction, when you remove the tube from the urethra, urine can leak out, which can lead to infection of the genital organs - this can cause serious inflammation.
By design, catheters are of the following types:
- Nelaton device, which is disposable. It is a soft tube with a rounded end. Apply when conducting rapid catheterization for diagnosis or before surgery.
- Foley system. Most often used in medical practice with prolonged use. It is a device from a thin tube and a tank for removing the liquid.
- Timann stent. This device is usually used in diseases of the genitourinary system.
Indications and contraindications
The most frequent indications for a drainage installation are as follows:
- emergency conditions that are associated with the need for the forced diversion of urine in case of problems with urination;
- specific diseases, when it is impossible to diagnose and begin treatment without catheterization;
- diseases that require using a catheter to either remove pus or inject medication.
But there are also contraindications:
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- injuries of the bladder or urethra;
- spasms in the urethra;
- no urine.

Preparing to install the device
So that the procedure does not end with complications, it is necessary to prepare for it. There are a number of conditions that will help to carry out quality work:
- attentive attitude to the patient by the doctor;
- sterility during catheterization;
- medical knowledge and skills;
- quality products.
Also, before catheterization, it is necessary to undermine the patient (it is obligatory - front to back), which will allow to avoid infection. Furacilin solution is best suited for this.
Also the doctor should prepare the following:
- catheter;
- anesthetic;
- capacity for removing urine;
- petrolatum, glycerin, which will facilitate the introduction process;
- expendables, including napkins, diapers, etc .;
- other tools: tweezers, syringe.
Bladder Catheterization Technology
Among women
In women, the procedure is usually easier and faster than in men, because the female urethra is not so long. The procedure is as follows:
- A nurse is standing to the right of the patient.
- Hand spreads labia.
- We treat the vulva with antiseptic.
- Introduces the inner end of the tube into the hole, treating it with vaseline.
- Checks the discharge, this will determine the correctness of the introduction of the catheter.
An important point: when pain occurs, you should immediately inform the doctor about it.
In men
The procedure in men is more complicated and time-consuming, since the length of the urethra can reach 25 cm, it is narrower, it has a lot of physiological narrowing, which prevents the tube from being inserted quickly and freely.
The procedure algorithm is as follows:
- A nurse is standing to the right of the patient.
- Treats the head of the penis with an antiseptic, paying special attention to the opening of the urethra.
- Using forceps inserts the end of the catheter into the urethra, holding the penis (the end of the tube should be lubricated with glycerin or another gel).
- Slowly and carefully moves him deep into.
- Upon reaching the narrowing points, the patient needs to take a deep breath, which will help to relax the muscles - this will allow the catheter to be introduced deeper.
- When spasms appear, the procedure is stopped until they pass.
With proper catheterization, urine will come out from the second end of the device.

In some cases, such as prostate adenoma, a soft catheter cannot be used; in such situations, a metal product is usually used. The technology is as follows:
- The doctor stands on the right side, treats the penis with an antiseptic.
- With one hand holds the penis in a vertical position, the second - introduces the end of the catheter so that its shaft is located horizontally.
- Carefully pushing the tube, as if pulling on her penis, until the end of the catheter does not fully penetrate the urethra.
- Tilts the penis to the abdomen, raises the end of the product and inserts the device to the very base.
- Sets the catheter in an upright position.
- Gently presses the end of the tube through the penis.
What can be complications
The risk of complications from an incorrectly performed procedure is very high. Catheterization is usually assigned without anesthesia, which allows you to notice the occurrence of pain in the patient. The most negative consequences of catheterization include:
- damage to the urethra;
- infection of organs (which can cause cystitis and even pyelonephritis);
- infection of the circulatory system in case of damage to the urethra;
- bleeding, fistula etc.
To avoid complications with prolonged use of the catheter, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of physicians. For example, you need to remember about the correct hygiene of the perineum, the catheter itself, otherwise complications may appear.
If a leakage of urine was detected or blood appeared in it, with severe discomfort, you should immediately go to the doctors. The removal of the catheter itself should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
With properly performed catheterization, many diseases can be diagnosed and cured at an early stage.