The bacterium Chlamydia psittaci, which leads to chlamydia, is very dangerous. Moreover, the symptoms of this disease can occur almost imperceptibly, because of which many pet owners are not in time to seek treatment. Because it is so important to monitor your pet, to know what symptoms, even the most minor, can indicate the presence of bacteria.

The concept of the disease and the mechanism of its development
Chlamydia is an infection that is caused by pathogenic microorganisms of the genus Chlamydia, which combine the features of both bacteria and viruses.
Due to the lack of energy metabolism, chlamydia enter the body of the host and "live" in the cells of the immune system or epithelial tissues. Favorite habitat - cells of the mucous membranes of the pharynx, intestines, urethra, stomach. Passing inside, microorganisms lead to failures in the work of the protective mechanism, which allows creating the most favorable conditions for reproduction.
Cell proliferation is carried out by binary division: the cell affected by the virus disintegrates, then it releases new parasites. This happens every two days.
The cells of the immune system spread chlamydia throughout the body, as a result of which infection of the brain or spinal cord, any internal organ, lymph nodes, and joints is possible.
Chlamydia in cats deserves special attention. There are the following ways of transmission of this infection:
- alimentary;
- aerogenic (airborne);
- sexual.
The cause of infection can be saliva, milk, urine, feces. Also, the infection can be transmitted from a sick animal during childbirth. The incubation period reaches two weeks.
 Chlamydia is clearly manifested in the following stressful situations:
Chlamydia is clearly manifested in the following stressful situations:
- when weaning the kitten from the mother;
- when you change your usual diet, etc.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the development of this infection:
- long stay of an animal in a confined space, for example in a shelter;
- reduced immunity;
- lack of vaccination.
The most common infection affects:
- eyes;
- respiratory system;
- digestive tract organs;
- reproductive system.
A generalized form of infection, in which a cat has a rapid spread of pathogens through the blood throughout the body, often leads to the death of the animal.
The main symptoms
External signs are largely dependent on the long-term presence of chlamydia in the body, on how strong the causative agent of infection is, which organs were damaged, and which state of the immune system.
The course of the disease can be chronic and acute, in the second case, the signs are more pronounced. At the onset of the disease, the temperature may rise slightly, and the infection usually does not affect appetite and general condition. In chronic form, there may be problems in the work of the heart.
Much depends on which organs and systems were affected.
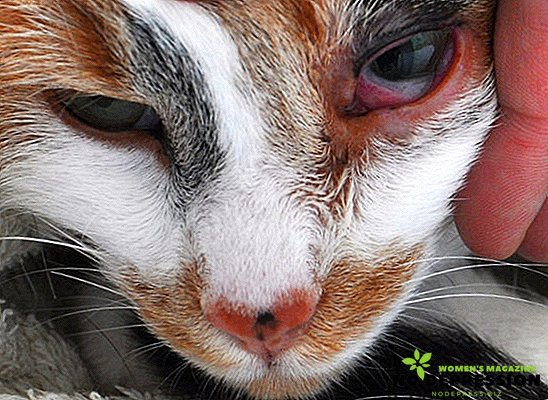
Eye damage:
- profuse tearing;
- conjunctiva swells, reddens;
- a third eyelid may appear;
- usually one eye is affected first, after which the infection passes to the second.
There is no cure for the disease; at first glance, conjunctivitis, which is usual at first glance, will turn into serious eye diseases leading to blindness - cataracts, keratoconjunctivitis, etc. The infection will become chronic. In this case, the eyes are usually reddened, and tearing occurs on a regular basis.
Respiratory lesions are characterized by:
- mucus from the nose;
- cough;
- shortness of breath and wheezing;
- possible development of pneumonia;
- fever
Sexual Chlamydia:
- may be asymptomatic;
- occasionally manifested by secretions from the vulva, but for most pet owners, this happens unnoticed.
With the defeat of the gastrointestinal tract, there are usually no symptoms, since the animal - the carrier of the infection - releases it with saliva and other fluids into the environment.
Treatment of chlamydia in cats
The diagnosis can be made only after a special analysis - only on the basis of one clinical examination it is impossible to make a diagnosis. Samples of genitals, eyes, and nose are sent to the laboratory.
Treatment in the early stages is simple, the main thing is to detect the infection in time and get expert advice. But if you try to cure chlamydia yourself, it can cause the disease to become chronic, and the microorganism will develop resistance to improperly chosen drugs.
 After the treatment regimen has been prescribed, any activities can be carried out at home in the absence of complications or difficulty breathing in the animal. An important point: if two cats live in the house or there are other favorite pets, the sick animal will need to be isolated.
After the treatment regimen has been prescribed, any activities can be carried out at home in the absence of complications or difficulty breathing in the animal. An important point: if two cats live in the house or there are other favorite pets, the sick animal will need to be isolated.
Treatment with antibacterial drugs and antibiotics should continue even after the symptoms of the disease disappear, i.e. at least 3-4 weeks.
But if you shorten the duration of therapy, chlamydia can develop resistance to drugs, which will complicate subsequent treatment. After the end of the course of therapy, an analysis of chlamydia is necessarily performed, since the absence of symptoms does not always indicate a complete cure.
Antibiotics
The most effective antibiotics of the tetracycline series, the rest are weaker and can be appointed additionally:
- Tetracycline - 7-12 mg / kg twice a day intramuscularly or 20 mg / kg orally through an equal amount of time. However, not all animals tolerate such drugs well. It is necessary to begin therapy with the minimum medical dose, gradually bringing to the desired therapeutic (for 3-5 days).
- Doxycycline - administered orally once a day at 5-10 mg / kg.
- Minocycline, Metacycline. Prescribe drugs similar to tetracycline.
- Levomycetin - 10 mg / kg up to three times per day.
Eye ointments and drops
Such preparations can be used after cleaning the eyes from pus or dry crusts. For this, either a ready-made saline solution or a chamomile decoction is suitable.
The following drugs will do:
- 1% tetracycline eye ointment, which is laid in the lower eyelid three times a day during the week;
- erythromycin ointment 10,000 U;
- chloramphenicol drops: instill 1 drop in each eye 3 times a day, the duration of therapy is at least a week;
- drops "Iris": they drop 2 drops into each eye 3 times a day for 10 days;
- Dect 2 drops: 2 drops in each eye twice a day - therapy lasts a maximum of 5 days.
Immunomodulators
Such drugs are usually prescribed for prolonged infection to increase the body's defenses:
- Gamavit: up to 3 injections per day at 0.1 ml / kg, the duration of therapy is 1 month;
- Immunofan: is administered 1 time per week, 1 ml per month;
- Maxidine: 0.5 ml / 5 kg of animal weight twice a day for five days.
Lactobacillus
It is desirable to use them during the entire course of taking antibiotics, especially if the latter are prescribed in the form of tablets. They will help avoid problems with the digestive tract:
- Laktobifid, Laktoferon: on 1 tablet 1-2 times a day;
- Lactobacterin: one hour before feeding, 1 dose (to be diluted in 1 tsp. Boiled water).
Features therapy kittens
Chlamydia can be sick kittens aged from 5 to 12 weeks. This is called chlamydia neonatal conjunctivitis. Symptoms occur when the kitten opens its eyes, and they are similar to the manifestations in adults. However, infection for kittens is more dangerous: they can quickly die.
And if the kitten has survived, but it has not been treated, then the disease can last for years without symptoms. But with a decrease in immunity, an animal can develop sluggish rhinitis and conjunctivitis. For many years, a pet can spread the parasites, therefore, having noticed the first symptoms of the disease in a kitten, it is necessary to cure him immediately.
Veterinary medicines try to prescribe mildly acting on the internal organs:
- Sinulox;
- Clavil;
- Amoxicillin, etc.
The kitten’s body is much weaker than an adult’s, so probiotics can also be prescribed with antibiotics, in order to avoid stomach problems.
Preventive measures - how to protect the animal?
The main danger of this disease is that it can be completely asymptomatic. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the issues of prevention:
- Do not allow your pet to communicate with street cats;
- when mating, request a chlamydia test from the pet of the second animal;
- visit the vet regularly;
- Do not forget about vaccinations.
Moreover, veterinarians strongly recommend vaccinating all animals, even if the owner is firmly convinced that his cat will not go out and will not be able to get sick anywhere. But only a healthy animal is allowed to be vaccinated, and the cat should also be treated for worms.
The following vaccines are most popular:
- Chlamycon;
- Multifel;
- Felovax-4;
- Katavak;
- Nobivac (Nobivac Forcat);
- Purevax RCPC.
Chlamydia is a dangerous disease that is caused by the penetration of the microorganism chlamydia into the body. In the absence of proper treatment and with a weakened immunity, this infection can be fatal. Because it is so important to know the main symptoms, in time to consult a doctor.