Tuberculosis is a very dangerous and widespread infectious disease in the world, which is caused by various mycobacteria - tuberculosis sticks (Koch sticks). Most often the disease affects the lungs.
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that the symptoms often appear only in the later stages and consist mainly in a prolonged cough with sputum and blood. Later, fever, night sweats, dramatic weight loss joins these symptoms.
What you need to know about tuberculosis
In the medieval era, tuberculosis was very common both in Europe and in Russia. Long before the discovery of the causative agent of this disease, doctors were aware of the extremely infectiousness of this disease and the almost futile attempts at treatment. Therefore, patients could only isolate.
Medicine is developing at a rapid pace, and today in the arsenal of doctors there are accurate and effective diagnostic methods, albeit complex, but effective methods of treatment. And most importantly, safe methods of prevention of the population exist and are successfully used in the fight against epidemics.
Most of the population of Russia is vaccinated against tubercle bacilli in the first days of life, while still within the walls of maternity hospitals, with the BCG vaccine (an active specific preventive vaccine), revaccination is carried out at the age of seven.
It is also common in society to take a regular test for tuberculosis - the Mantoux reaction. Now we can not be afraid to face this disease in public transport or in the store.
How do you get infected and who is prone to the disease in the first place?
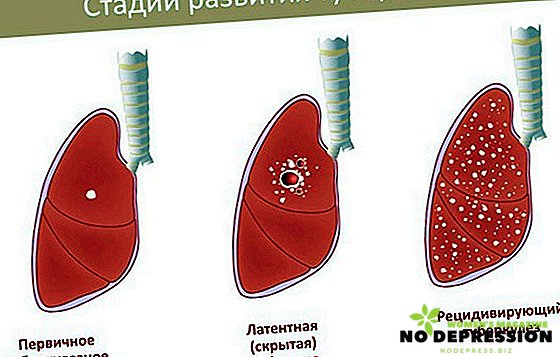
There are two main forms of the disease according to the degree of contagion:
- Open form. This term means that a patient releases microorganisms that cause tuberculosis to the environment.
- Closed form. A patient with such a form cannot infect people.
As it is known, one person, sick with an open form of tuberculosis, is able to infect up to twenty healthy and unvaccinated people a day. Infection occurs instantly through the entry of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through personal contact, by airborne droplets, and also by household means (through dishes, a door handle, or an elevator button).

Koch Wand
The tubercle bacillus is so tenacious that it is not afraid of any changes in temperature, or sunlight, or water. It can exist in the heat and in the cold, on clothes, books, dishes, towels for up to three months. Also, animals, insects, birds can carry tuberculosis. They can become infected by eating the meat and unboiled milk of a sick animal.
The World Health Organization (WHO) claims that about one third of the total population of the world is infected with mycobacteria in various forms. And every year about two million people die from this disease, and eight million become infected.
Of course, the first in the list for tuberculosis morbidity and mortality are countries with a low standard of living, underdeveloped and densely populated. But according to data for 2014, 60 people per 100 thousand of the population are falling ill in Russia.
In fact, nobody is insured against tuberculosis. They are sick of people of any age and gender, any social status. However, scientists note that the risk of getting sick can affect:
- Working conditions (stresses, excessive loads);
- Age (18-26 years old, children, elderly);
- The presence of bad habits (smoking);
- Diabetes;
- Immunity weakened by other diseases;
- The presence of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).
Tuberculosis: symptoms and early signs of the disease in adults
Most of the people who are carriers of Koch sticks, are not aware of the processes occurring in their body. Often, the pathogen is detected by chance, on scheduled examinations (photofluorogram or mantle reaction).
A person with an initially weakened immunity, meeting with the carrier of the open form of the disease is infected instantly.
The first signs of infection can be: constant weakness and a slight increase in body temperature
Also, any seemingly healthy person should be alerted by the manifestation of symptoms such as:
- Disorders of the central nervous system (Irritability, irascibility, apathy, mood variability, absent-mindedness). Tuberculosis bacillus, entering the body, is localized in the lymphatic system, liver, kidneys, joints and causes intoxication of the body and, as a result, disorders of the central nervous system (central nervous system);

- Vegetative disorders (arrhythmia, heart failure, increased night sweats, jumps in body temperature);
- Swollen lymph nodes (usually cubital / ulnar and supraclavicular). Lymph nodes are enlarged, soft-elastic, mobile, as the disease spreads, they become harder and stiffen.
If a person’s immune system is strong enough and is able to cope with the disease on its own, then all the symptoms disappear and the inflammatory response subsides. Koch's wand is excreted from the body and the person is considered completely healthy.
Otherwise, the symptoms of intoxication are joined (as the disease progresses):
- Cough, especially obsessive in the evening;
- The temperature is slightly above normal (usually within 37-38 degrees);
- Expectoration of blood and mucus;
- Weight loss;
- Loss of appetite;
- Heart palpitations;
- Bitonal cough - dry, deep, with a characteristic double sound (it is squeezed by enlarged lymph nodes of the bronchi and trachea);
- Obstructive bronchitis (which is not amenable to conventional medical treatment);
- Allergic rash;
- Confusion, delirium (caused by a lesion of an infection of the central nervous system);
- Wheezing.
What to do if you suspect tuberculosis in yourself or your loved ones?
If any suspicious cough appears (even if a person coughs twice a day, but it lasts more than three weeks), a prolonged “cold”, with loss of appetite and a sharp weight loss, you should immediately contact a physician for help and tell about all the troubling symptoms .
If you don’t really want to go to the doctor, you can do a Mantoux skin test at any paid medical center. This reliable method can show whether a tubercle bacillus is in the body.
How can a doctor confirm the presence of a pulmonary tuberculosis bacterium?
Due to the fact that tuberculosis may not manifest itself for a long time, doctors very often discover it by chance. When conducting x-rays, chest x-rays, tuberculin specimens, the presence of tuberculous mycobacterium in the body will not go unnoticed.
If a patient goes to the doctor with complaints and symptoms similar to the clinical picture of a patient with tuberculosis, he needs to undergo a series of examinations:
- General examination of the patient. On examination, the presence of features characteristic of patients with a progressive form of tuberculosis is revealed: pallor of the skin, a specific blush, and gleam in the eyes. Expanded intercostal spaces, protruding shoulder blades are also characteristic of advanced cases;
- Check for two scars from the BCG vaccine;
- Survey (social status, the likelihood of contact with patients, the presence of chronic diseases, immunodeficiency);
- Chest x-ray / fluoroscopy;
- Smear for microscopic examination of sputum. Unfortunately, a negative result does not indicate the absence of infection, so this procedure is recommended to be carried out three times;
- General blood analysis. Typical changes for a patient with tuberculosis will be: anemia (decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin), leukopenia (moderate decrease in the number of white blood cells);
- Sputum culture. This analysis takes a very long time (about three months), but allows not only to detect the presence of an infection, but also to immediately determine the sensitivity of the bacterium to antibiotics.
Methods of treating tuberculosis in adults
Tuberculosis is treated by a TB doctor.
Koch's wand is resistant to antibiotics, therefore, at the moment, poly component tuberculosis chemotherapy is considered the most popular and effective treatment method. Today, two treatment regimens are used - four-component and five-component chemotherapy.
In these schemes, the most modern antibiotics (rifampicin or rifabutin) and tuberculosis chemotherapy drugs (isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) are used.
An important additional tool in the treatment of tuberculosis is a sanatorium stay. It has long been known that mycobacteria poorly survive in conditions of a large flow of oxygen into the lungs.
Therefore, living in a discharged air of mountain resorts has a beneficial effect on the healing process. Also, doctors recommend to follow a diet (high-calorie, varied diet with an emphasis on dairy and dairy products, rich in potassium salts).
To restore the strength of the body after an illness, treatment with koumiss - mare's milk is used. It is believed that this product, rich in microelements and vitamins, contributes to the improvement of the digestive system and weight gain.
In advanced cases, surgical treatment methods are used: removal of the lobe of the affected lung or lung entirely, artificial pneumothorax (introduction of oxygen into the lungs) and pneumoperitoneum (introduction of oxygen into the abdominal cavity).
In the event that treatment was started on time and carried out qualitatively, one can count on full recovery, however, no physician can guarantee that there will be no recurrence of the disease. With late treatment, therapy helps poorly and the result will be disability and death.
What precautions and preventive measures exist
In the earliest childhood in our country, a program begins to protect the population from all forms of tuberculosis. BCG vaccine (prepared from a live strain of a weakened bovine tubercle bacillus, which is grown artificially and is not dangerous to humans) vaccinates children on the third day of life and at the age of seven.
In order to early diagnose possible diseases of tuberculosis, every conscious citizen should undergo a free fluorography examination once a year to identify foci of infection in the lungs.
You should also follow the rules of personal hygiene, eat in proven places, use only pasteurized or boiled milk for food, and carefully monitor the quality and readiness of meat products.
You can learn more about the symptoms of tuberculosis from the following video.