Varicose veins is a chronic disease in which the veins are subject to knotted dilation. At the same time, disturbances can occur in the outflow of blood, its stagnation in the venous system. As a result, the veins on the lower limbs protrude. However, varicose veins is one of the forms of this disease, since the problem can affect other organs, parts of the body.
Causes
Why does varicose veins appear and what is it? The main factors of development are genetic predisposition, gender. Women, because of their love for heels, taking contraceptives, are victims of this disease twice as often.
Also the development of this disease contributes to the following:
- Hereditary factors in which it is not the disease itself that is transmitted, but the structure of the veins (weak tissues, defective valves), in which the risk of varicose veins increases. It is for this reason that these pathologists can occur not only in adults but also in children.
- Hormonal changes usually affect women. The most dangerous periods at which the risk of developing pathology is as high as possible is the period of pregnancy and the postpartum period. Dangerous and climax. And all this is due to the fact that there is not enough estrogen in the female body — instead, they are dominated by the yellow body hormones, which have a relaxing effect on the muscles.
- Sedentary lifestyle, long standing. Also affects age, because over time, the walls of the veins, the valves become thinner, their work is disturbed.
- Equally important is the weight - the presence of extra pounds has a serious load on the veins of the legs, which can cause an unpleasant disease.

However, there is also varicose veins of the esophagus, small pelvis and uterus. The causes of these pathologies are slightly different. If we talk about the esophagus, then the main reasons that can lead to this problem include hypertension, liver cirrhosis, and hereditary factors also affect.
Varicose veins of the uterus are usually associated with:
- increased progesterone levels;
- increased load on the pelvic organs;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the uterus;
- artificial interruption of pregnancy.
If we are talking about pelvic organs, then the following causes lead to varicose veins: inguinal hernia, tumors, gynecological diseases, dysplasia, prolonged use of contraceptives.
Stages of varicose veins in the legs
There are three stages of progression of this disease:
- Compensation, in which there are no complaints, unpleasant symptoms, and when viewed from patients can observe dilated veins in the legs.
- Subcompensations. In this case, when examined by a doctor, pronounced varicose dilatations will already be noticeable, patients may complain of goosebumps, cramps at night, swelling of the feet and ankles is observed.
- Decompensation. At this stage, the appearance of eczema and dermatitis is added to the above symptoms, and the itching of the skin begins to disturb patients.
It should be noted that the varicose veins itself is not dangerous, but if it has already appeared, then it will not pass on its own, it may cause more serious complications, which are dangerous.
The main signs of pathology
Symptoms in each case will be different. But it is very important to accurately determine the signs in order to consult a doctor in time and begin treatment.
Lower limbs
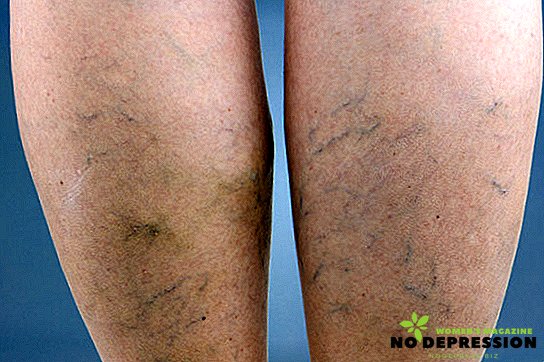
The first signs of varicose veins on the legs include:
- fatigue;
- swelling of the lower limbs;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- vascular "stars";
- prominent veins and the appearance of seals.
Pelvic Organs
 The symptoms of this disease include:
The symptoms of this disease include:
- the appearance of chronic pain, which is mainly localized in the lower abdomen, can give in the groin;
- discharge, which is typically a female symptom - usually do not have a smell, but the number of patients can be alerted;
- the appearance of spider veins on the hips, in the crotch area (for men, on the penis);
- problems with the menstrual cycle in women, urination disorders.
Esophagus
The most common symptoms are:
- heartburn;
- belching;
- difficulty swallowing;
- discomfort and heaviness in the chest;
- cardiopalmus.
Uterus
Symptoms:
- lingering back pain;
- pain when urinating;
- sensitivity of the vaginal walls;
- discomfort during intercourse, physical exertion;
- menstrual problems;
- gut feeling
Prevention of varicose veins
If you have a tendency to this pathology, to slow its progression, you need to follow these guidelines:
- comfortable shoes should be worn without heels or low heels;
- during loads, special bandages should be used on the legs, but only after consulting with a doctor;
- try not to sit or not to stand for a long time in one place, try to move, warm up;
- do not take too hot baths - better replace them with a douche;
- stop smoking and other bad habits
Rules for the treatment of varicose veins
On foot
In many ways, the treatment of varicose veins on the legs is carried out for cosmetic purposes. There are the following methods to get rid of this problem:
- Sclerotherapy, involving the introduction of a special drug, filling a vein, due to which it begins to disappear. To completely solve the problem, up to 5 sessions are required.
- Non-surgical treatment using special elastic stockings (carried out only at the initial stage). They help to pass the veins, keeping them from stretching, reduce pain.
- Drug treatment, which aims to reduce symptoms, pain, slows the development of varicose veins. Such drugs as Venitant, Ascorutic Forte, Gepatrombin, Troxerutin are usually prescribed.

Venotonic preparations may also be prescribed.
- Detralex;
- Phlebodia;
- Eskuzan.
Esophagus
The main task in the treatment is the treatment of the underlying disease and the prevention of the appearance of bleeding. To do this, prescribed medications, vitamins, antacids, as well as the mandatory prevention of esophageal reflux.
In the case of bleeding, hemostatic therapy is performed, in which calcium preparations, plasma, and vitamin K are prescribed. To stop the bleeding, they can prescribe the administration of the Blackmore probe, which overlaps the vessels.
Small pelvis
In this case, treatment will be directed to:
- cessation of reverse blood flow;
- normalization of the tone of the veins;
- improving blood supply to tissues;
- removal of pain symptoms.
Therapy includes components such as:
- medication in case of exacerbation;
- regular use of physical therapy methods, which will prevent relapses.
Conservative treatment with venotonic can also be prescribed.
In rare cases, an operation is prescribed - if the disease is neglected, there is a predisposition to varicose veins. Surgery involves the following procedures:
- ligation of the ovarian vein;
- ligation of the genital vein;
- Troyanova-Trendelenburg operation.

Uterus
In the case of making a diagnosis of uterine arterial vascular disease, treatment involves changing the mode of exercise, reducing sedentary work, and normalizing diet. Also, experts often recommend the use of compression tights, which reduce pain, normalize blood microcirculation.
Also, uterus varicosity requires the use of the following medications6
- vetonik - medicines that strengthen the walls of blood vessels, have anti-inflammatory effect, for example, Detralex;
- angioprotectors - strengthen blood vessels, improve microcirculation, reduce vascular permeability (Troxevasin);
- enzyme preparations that are aimed at improving the metabolic processes in the body;
- nitrate-based medications to eliminate cramps.
In this disease, it is desirable to consult a doctor in time, because in this case the therapy will be easier.












