Healthy blood glucose is the key to productive physical and mental labor. What are the best indicators of sugar, what they can testify and how to adjust them?
Blood Glucose Norm: Hypo-and Hyperglycemia
The main task in carbohydrate metabolism is performed by metabolites and glucose: they provide the tissues of the body with energy and support cellular respiration. Changes in blood glucose levels — raising or lowering — have a negative effect on human health.
Controlling the level of sugar allows you to avoid a number of dangerous consequences for the body.
Short course: the role of glucose in the human body
It is known from the school chemistry course that sugar, like its carbohydrate congeners, cannot be assimilated by the body without prior splitting. In the aquatic environment, special enzymes that recognize the ending "-az" in the name, affect the chemical structure of sugar, changing it to glucose compounds.
The pancreas and small intestine are responsible for the assimilation of sucrose split by glucose into the human body.
Glucose support needs skeletal muscles, cardiovascular and central nervous systems. To maintain a normal level of "sugar" allows proper nutrition and inclusion in the diet of foods rich in carbohydrates.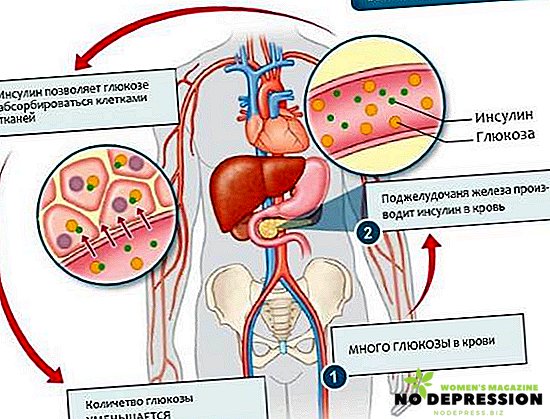
Deviations from the regulatory limits of the content of glucose compounds entail a number of serious consequences.
- Low blood sugar leads to energy starvation of cells, which, in turn, limits their functional abilities. In cases of development of chronic diseases associated with glucose starvation, a person is threatened with brain or nerve cells.
- Excess of healthy norms provokes the postponement of glucose and the subsequent damage of proteins of tissues. In patients with hyperglycemia - elevated blood sugar levels - there is destruction of tissues of organs such as the kidneys, eyes, heart, and blood vessels. A huge blow to the nervous system takes.
Test procedure
To investigate the level of glucose compounds in the blood, two methods help: a blood test for glucose (sugar), performed on an empty stomach and with a sugar "load." The value of such measures has both preventive and therapeutic meaning: passing tests helps diagnose a number of diseases, including:
- obesity;
- pathology of internal organs;
- the development of hyper and hypoglycemia;
- diabetes prevention and monitoring.
 The attending physician is repelled by the results obtained, makes a diagnosis or, if there is a fraction of a doubt, sends for additional laboratory tests to study the hormonal and enzymatic background of the patient's body.
The attending physician is repelled by the results obtained, makes a diagnosis or, if there is a fraction of a doubt, sends for additional laboratory tests to study the hormonal and enzymatic background of the patient's body.
The most common continuation of the standard glucose test is the sugar tolerance test.
The essence of this method is reduced to the delivery of two types of blood to patients: on an empty stomach and after taking a certain amount of glucose.
Blood glucose concentration: adults, pregnant women, children
The level of glucose in the blood reflects the state of the body and allows you to warn the development or diagnosis of disease. The average normal concentration of glucose in the blood is 5.5 mmol / liter.
However, after analyzing the level of glucose in the blood, the results are compared with a table of healthy sugar content, depending on the age of the patient.
The rate of blood glucose in children, women and men - a table by age:
| Age | Lower and upper limits of normal blood sugar, mmol / liter |
| 2 days - 4.3 weeks | From 2.8 to 4.4 |
| 4.3 weeks - 14 years | From 3.3 to 5.6 |
| 14 - 60 years | From 4.1 to 5.9 |
| 60 - 90 years | 4.6 to 6.4 |
| Over 90 years old | 4.2 to 6.7 |
More accurate test results for glucose in the blood of a child’s body should normally have the following lower / upper thresholds:
| Child's age | Blood sugar, mmol / l |
| Up to 2 years | 2,78 - 4,4 |
| 2-6 years | 3,3 - 5 |
| School children | 3,3 - 5,5 |
In most cases, if the conditions of the tests carried out were met, and their indicators fluctuated within 5.5 - 6.1 mmol / l, the attending physician prescribes a referral for an additional examination - glucose tolerance. Only after this test, a specialist can make a diagnosis.
 Pregnancy leads to significant changes in the female body. Thus, the average rate of blood sugar in pregnancy is 3.3 - 6.6 mmol / liter.
Pregnancy leads to significant changes in the female body. Thus, the average rate of blood sugar in pregnancy is 3.3 - 6.6 mmol / liter.
The movement beyond these coefficients is indicative of the development of gestational diabetes, which, due to an increase in the number of ketone ones and a decrease in the level of amino acids, may turn into type 2 diabetes in the postpartum period.
By the 28th week, an oral hourly glucose test is recommended. The optimal result is an indicator not exceeding a figure of 7.8 mmol / l. If there is an increase in sugar content, a test of three hours is carried out, during which the dose of glucose increased twice as compared with the previous analysis is administered to the pregnant woman. The result of taking 100 g of glucose should not exceed the following indicators:
| Test duration | Maximum level of glucose norm |
| 1 hour | 10.5 mmol / l |
| 2 hours | 9.2 mmol / l |
| 3 hours | 8 mmol / l |
Sugar is not normal: the causes of hyper- and hypoglycemia
The content of glucose in the blood depends on many factors. Fundamental in this aspect is the daily menu, the degree of physical and mental work, the natural susceptibility of the pancreas to the production of insulin, which is responsible for lowering sugar, and the production of hormones in the body that neutralize insulin.
We see that, in addition to "external" factors, an important role is played by the structure of the human body in the individual case.
As a raw material for the synthesis of glucose is used:
- lactic acid: it hides in the muscles that were under pressure and red blood cells;
- glycerol: formed due to the fermentation of adipose tissue;
- amino acids: are formed due to protein breakdown (muscle tissue).
 It is worth noting the danger of the body synthesizing glucose through the use of amino acids, which is actually eating your own muscle tissue. There are cases of "self-devouring", reaching the heart, the smooth muscles of the intestine and the vascular system.
It is worth noting the danger of the body synthesizing glucose through the use of amino acids, which is actually eating your own muscle tissue. There are cases of "self-devouring", reaching the heart, the smooth muscles of the intestine and the vascular system.
Why can blood glucose levels be raised or lowered? The causes of low or elevated blood glucose levels may be hidden in the endocrine system abnormalities, as well as the pathologies of organs such as the pancreas, kidneys, and liver.
Significant impact on the degree of "sugar content" of the blood have diseases transferred or currently transmitted by humans: heart attack, stroke, diabetes. Characteristic "poginizer" insulin levels, in addition to the above, are poisoning by alcohol or chemicals, overdose by insulin, steroids, amphetamines, vegetative disorders, malignant tumors.
The sugar content of prolonged fasting, combined with excessive physical exertion, decreases.
Way back to healthy indicators
A person who has set himself the goal of returning blood sugar levels to normal levels should prepare for active and hard work on himself, adjusting habits and lifestyle.
 Minor deviations from the established standards require a healthy diet. So, the patient's diet of hyperglycemia should include a minimum of carbohydrates. Foods that are high in sugar, bakery and pasta made from high-grade wheat flour, potatoes, wine and sodas fall under the food taboo.
Minor deviations from the established standards require a healthy diet. So, the patient's diet of hyperglycemia should include a minimum of carbohydrates. Foods that are high in sugar, bakery and pasta made from high-grade wheat flour, potatoes, wine and sodas fall under the food taboo.
It is important to take care of the introduction into the daily menu of vegetable "opponents" of sugar: cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, pumpkins, and so on.
The dosage of sugar substitutes that are actively attracting the attention of diabetics should be prescribed by the attending physician: excessive use of these substances can lead to disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and the development of a deceptive feeling of hunger.
Hypoglycemia - an insufficient level of glucose in the blood - also requires an adjustment of food culture. The ration should be aimed at the use of high-protein products (nuts, beans, dairy and meat non-fat products).
Accordingly, a full examination, an integrated approach and the preparation of an individual course of therapy are required.
Drugs in the fight against hyperglycemia are aimed at smoothly reducing sugar levels without increasing insulin production. In most cases, the attending physician prescribes agents such as sulfonylureas and biguanides.
Additional information about the rate of glucose in the blood - in the next video.