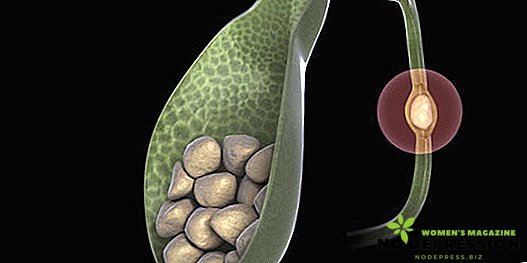
Polyposis of the gallbladder is a pathological process that leads to the appearance of tumors on the surface of the mucous membrane of the organ. This disease does not apply to oncological diseases, however, the lack of competent treatment can cause a benign education to become malignant.
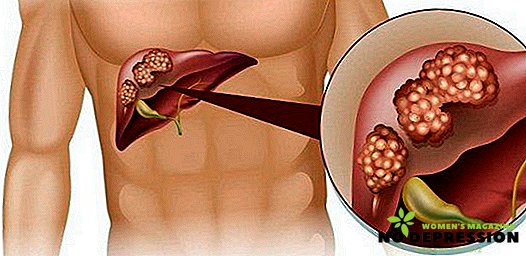
Causes of polyp formation
The formation and growth of polyps can develop for various reasons. But there are the most common:
- Hereditary factor. He plays an important role. If the relatives already had papillomas, adenomatous tumors, the risk of polyposis increases.
- Inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. One of the most serious diseases that can lead to the development of polyps is cholecystitis. On its background, there is stagnation of bile, which causes a thickening and change in the walls of the organs. In the inflammatory process, the gallbladder tissue reacts to any changes, modified. Cells of the walls begin to grow, which eventually becomes the cause of the formation of polyps.
- Violation of metabolic processes. Often, polyposis causes a violation of lipid metabolism. This leads to the circulation of large amounts of cholesterol in the blood. An excess amount leads to its accumulation and deposition on the vascular walls and in the organ itself. As a result, cholesterol polyps appear. The problem is that their formation and growth is almost asymptomatic.
- Diseases of the biliary tract. Any disturbance that is associated with this organ leads to an imbalance between the amount of bile and its volume. With a lack or excess of bile, serious consequences can occur, which are characterized by diseases of the digestive tract organs. And the appearance of polyps is one of them.
Classification
Most often, polyps are located on the mucous membrane of the walls of the gallbladder, fasten with a broad base or leg, a bubble grows.
Since the symptoms of their appearance are similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is very difficult to diagnose pathology.
There are the following types of formations:
- Adenomatous. In this case, benign polyps. Their growth provokes the growth of glandular tissues. Polyps tend to transform into malignant tumors. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor as soon as possible, who can exercise constant control over them.
- Papillomas. Are benign education. But due to the papillary shape can be transformed into a malignant tumor.
- Polyps of inflammatory nature, the appearance of which provoke various factors that irritate the mucous membrane of the organ. The reasons may even be parasites. This form is not tumor, because polyps are provoked by inflammatory phenomena.
- Cholesterol polyps. These formations appear on the background of excess cholesterol in the blood, in violation of fat metabolism in the body. The most common today are cholesterol polyps, which are treated with conservative methods of therapy.
Symptoms - what to look for?
The signs of the disease depend on where the tumor is located. The most unfortunate arrangement is in the cavity of the duct or the neck of the organ. This leads to obstruction of the pathway of bile, which can cause secondary pathology - obstructive jaundice. If polyps are located in other areas, the patient may not experience any characteristic signs of the disease.
However, there are a number of symptoms by which this disease can be recognized:
 Pain that is provoked by various factors, for example, stretching of the walls of the organ and stagnation of bile. Pain can be aching, dull, giving to the right hypochondrium. Often the pain appears after drinking alcohol, junk food, stress.
Pain that is provoked by various factors, for example, stretching of the walls of the organ and stagnation of bile. Pain can be aching, dull, giving to the right hypochondrium. Often the pain appears after drinking alcohol, junk food, stress.- Hepatic colic. Usually appear if polyps are located in the neck of the organ. The patient usually experiences severe pain. In addition, there may be signs such as rapid pulse and heartbeat, increased pressure.
- The skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow. Due to the fact that the tumor tightens the bile ducts, obstructive jaundice can occur. In addition, it can cause allergic reactions: itching, rashes, skin irritation. Urine usually darkens, there may be vomiting with bile, body temperature rises.
It is worth noting that such signs speak of significant irregularities in the digestive tract. However, many patients are not in a hurry to see a doctor, and the disease and the cause of a polyp can only be determined by diagnostic methods.
Is there a connection with other diseases?
Polyps of the gallbladder are often found when the patient complains of unpleasant symptoms. The patient must be carefully examined, to conduct a full diagnosis. Only an abdominal ultrasound can reveal the presence of tumors.
Most often it is:
- Pancreatitis. This is an inflammation of the pancreas, which is manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium. Nausea, vomiting, stool is disturbed.
- Chronic cholecystitis. Most often, this disease occurs due to a bacterial inflammatory process. But even parasites can cause it.
- Cholelithiasis. With this disease, stones are formed in the gallbladder cavity or ducts due to lipid metabolism disorders.
How is the diagnosis?
There are the following methods for diagnosing polyposis:
- Ultrasound. The tumor is viewed using special equipment. Due to the modern technique, all organs of the abdominal cavity can be fully considered.
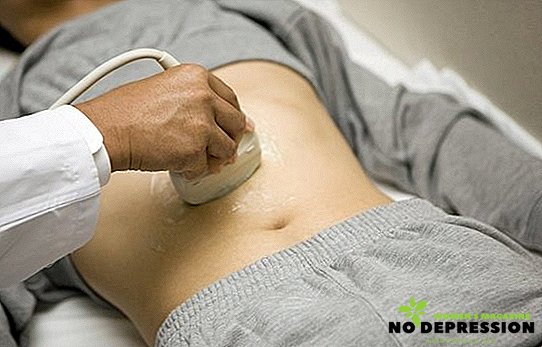
- Ultrasonography. This procedure is carried out through the oral cavity, into which a special tube is inserted - an endoscope with an ultrasonic sensor. With this device you can detect polyps, explore the organ cavity. This method is the most accurate.
- Cholangiography. The study is performed using tomography. Very convenient and painless way to detect the disease, helps to figure out the size, location of polyps.
Also conducted a study of blood, urine and feces.
Treatment of gallbladder polyposis
Drug therapy
But it is worth remembering that self-medication should not be done, only the attending physician can prescribe medicines. Most often prescribed such drugs as:
- Ursofalk This tool quickly destroys cholesterol deposits and removes them from the body without complications.
- Holiver. Helps eliminate bile stasis.
- No shpa. This drug can be called auxiliary, because when it is taken the smooth muscles of the bladder relaxes. Due to this, spasms are stopped, normal duct patency is ensured. All digestive processes are normalized.
- Ursosan. This tool helps break down stones, but only if the gallbladder retains its function.
However, it is worth remembering that traditional conservative treatment with medications is prescribed only if the stones are no larger than 1 cm. If they are large, they grow quickly, they prescribe a surgical procedure that removes both the masses and the gall bladder.
Operative intervention
If traditional methods of treatment were not effective, there is a further growth and increase in neoplasms, surgical intervention is prescribed by doctors.
The problem is that any tumor growths can lead to the development of cancer, so they need to be constantly monitored and studied. In some cases, the operation can be assigned immediately after the examination: in the presence of large stones or if their number exceeds the permissible norms.
There are the following types of intervention:
- Laparoscopy. This operation is performed using special tools without surgical incision. Laparoscopy removes the gallbladder.
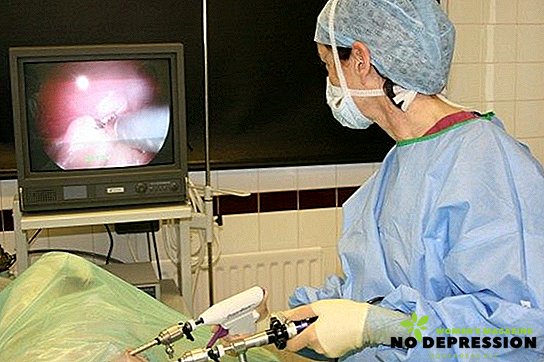
- Cholecystectomy. The standard technique is made by making a cavity incision through which the doctor penetrates the abdominal cavity to remove formations. The main disadvantage of the technique is a high level of injury, as there is a scar.
- Endoscopy. This operation is performed to remove the stones with the preservation of the body. To do this, use a geometric loop, which removes the growth.
Features of the diet
In this disease, a nutritionist or gastroenterologist prescribes a special diet. Its essence is to reduce the amount of harmful products in favor of healthy and less calorie foods.
Most often appointed dietary table number 5. The composition of permitted dishes include only fresh and healthy products. The purpose of proper nutrition in this disease is the most benign regimen, saturation of the body with beneficial vitamins, elimination of cholesterol.
Nutritionists recommend eating more vegetables and fruits, from them you can make soups, compotes, kissels, serve as a side dish. You can cook healthy puddings based on berries and fruits. It is recommended to include in the diet of fresh juices, diluting them with water.
From the diet should exclude products containing preservatives, dyes, enhancers, other harmful additives. It is necessary to refuse fatty, fried, spicy, salty, smoked food. And all products can only be boiled, stewed, baked, steamed.
Treatment by folk methods
Traditional medicine also has provided some methods of treatment of gallbladder polyposis.
Immortelle
 To prepare the decoction, you need to take 20 g of immortelle flowers, St. John's wort, blackberry leaves, plantain, 15 g of dill seeds and succession, 25 g of mother and stepmother leaves, strawberry leaves, 40 g of wild rose. All ingredients need to grind, mix.
To prepare the decoction, you need to take 20 g of immortelle flowers, St. John's wort, blackberry leaves, plantain, 15 g of dill seeds and succession, 25 g of mother and stepmother leaves, strawberry leaves, 40 g of wild rose. All ingredients need to grind, mix.
Take two tablespoons of the mixture, pour 500 ml of cooled boiled water, leave to infuse for 30 minutes. The broth should be drunk after filtering during the month at 70 ml for 30 minutes before each meal.
Celandine
Pour one tablespoon of dry celandine into a thermos, add 250 ml of boiling water. After a half to two hours, strain the broth and take it 3 times a day before meals, 2 teaspoons. The term of treatment is a month, after which you need to take a break for 10 days, and then resume the course for a month.
An infusion of celandine and chamomile can also help. Take the grass equally, chop, mix. One tablespoon of the mixture pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave overnight. In the morning, be sure to strain and in the morning take one teaspoon half an hour before breakfast.
Nasturtium
The following herbs are needed for cooking: tansy, wormwood, marigolds, nasturtium, manchurian leaves. The treatment regimen is as follows: you need to prepare and take an infusion of each herb separately for 28 days. In this case, change the sequence of herbs is impossible. Take one teaspoon of one of the herbs, pour 500 ml of boiling water, strain in half an hour. Take three times a day, 70 ml before meals.


 Pain that is provoked by various factors, for example, stretching of the walls of the organ and stagnation of bile. Pain can be aching, dull, giving to the right hypochondrium. Often the pain appears after drinking alcohol, junk food, stress.
Pain that is provoked by various factors, for example, stretching of the walls of the organ and stagnation of bile. Pain can be aching, dull, giving to the right hypochondrium. Often the pain appears after drinking alcohol, junk food, stress.