Very often, young mothers are faced with a situation where, after birth, the skin of their crumbs turns yellow. Panicking in this case is not worth it, because it is just a manifestation of the yellow one, which is typical of most newborns. Let's look at how this phenomenon takes place and what are its features.
Zheltushka - what is it?
To say that the yellow one is a disease is by no means impossible; it would be more correct to call it a syndrome characterized by yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. It can appear as a result of an increase in the blood level of bilirubin, which subsequently leads to an increase in its tissues.
 This pigment results from the destruction of red blood cells. Enzymes that are produced by the liver help to remove it from the body. The color of staining depends on the amount of bilirubin, the higher its level, the more intense the color will be.
This pigment results from the destruction of red blood cells. Enzymes that are produced by the liver help to remove it from the body. The color of staining depends on the amount of bilirubin, the higher its level, the more intense the color will be.
The production of pigment occurs in the body constantly. The first days of newborn children are adapting to the world around them, and due to the peculiarities of their physiology, bilirubin is released an order of magnitude slower.
That is why many babies have a yellowish skin tone.
Zheltushka in newborns: norm indicators
Norms bilirubin for newborn babies depend on their age and have the following indicators (µmol / l):
- the first hours of birth - should not exceed 51-60;
- the first week the rate rises significantly, but not higher than 205. For premature babies, his critical mark should be no more than 170;
- Starting from the 3rd week, the figures drop to 8.5 - 20.5.
In cases where during the first three weeks in full-term babies, the pigment level shows more than 256 micromol / l (for premature babies, this indicator should be above 172), here we can safely speak of pathological jaundice. Babies should be sent to a hospital for a full examination and prescription of drug treatment.
The causes of yellowing in newborns
The majority of newborns on the third or fourth day may experience physiological jaundice. As a rule, it does not bring any harm, and in duration it can be about three weeks.
If you had a premature birth, then such a syndrome can be delayed up to 1.5 months. It does not carry any danger and since time disappears by itself.
 A sharp increase in bilirubin can occur due to hypothermia baby, or malnutrition. Also provoke jaundice may discharge of original feces. The most effective prevention of this phenomenon is the early attachment of the baby to the breast.
A sharp increase in bilirubin can occur due to hypothermia baby, or malnutrition. Also provoke jaundice may discharge of original feces. The most effective prevention of this phenomenon is the early attachment of the baby to the breast.
The first milk (or colostrum) contributes to the removal of meconium, and with it bilirubin will be removed. In connection with this phenomenon, young mothers from the first hours of life of the crumbs, it is advised to teach him to breast milk.
Literally in 1% of cases, jaundice can result from overeating or overweight. Often it appears no earlier than the first week. This case is also called physiological.
 If you notice an increase in pigment in the body of your baby, then immediately need to stop breastfeeding for about two days. The diagnosis can be considered confirmed with a clear decrease in the yellowness of the baby.
If you notice an increase in pigment in the body of your baby, then immediately need to stop breastfeeding for about two days. The diagnosis can be considered confirmed with a clear decrease in the yellowness of the baby.
Feeding a newborn these days should be carried out with the help of expressed milk. Pre-sterilize it in a water bath for at least 5 minutes.
In addition to physiological jaundice, which does not bear any harm, the child may also be pathological. The main reasons that result in this type of jaundice, include the following:
- Mom and newborn have different blood types or as a result of Rh-conflict;
- Small hemorrhages;
- During pregnancy, the woman took a large amount of drugs;
- Infections that have arisen in the period of childbearing;
- Births earlier than 36 weeks;
- If your baby is bottle-fed;
- Disease mom diabetes;
- If the baby swallows some blood (as an option from nipple cracks during feeding).
Types and symptoms of the disease
 After the diagnosis, doctors can identify several types of jaundice in a newborn. This moment is very important, and without laboratory analysis it can sometimes be difficult to determine what type it is.
After the diagnosis, doctors can identify several types of jaundice in a newborn. This moment is very important, and without laboratory analysis it can sometimes be difficult to determine what type it is.
Depending on the results obtained, a specific treatment is prescribed. All cases of zheltushki can be divided into physiological and pathological, which in turn are divided into subgroups.
Physiological jaundice is normal for newborns, as the body tries to adapt to the new habitat. It occurs in the first weeks of age and does not have serious consequences. In turn, it is divided into the following types:
- Creatine jaundice in babies manifests itself later when creatine levels are exceeded in the food products of a nursing mother. This substance is contained in products of orange color (carrot, pumpkin, citrus);
- breast milk jaundice can occur when breast milk contains large amounts of estrogen. Initially, the work of the liver is aimed at removing estrogen, and later - on bilirubin. In this case, the yellowness of the skin can persist for about three months, while in no way affecting the development of the child;
- neonatal - this type is most common. It absolutely does not need to be treated. It eventually goes away on its own without any complications.
Pathological jaundice is the second main type, but its manifestation is already associated with all sorts of diseases of the internal organs of the crumbs. It is divided into the following types:

Rhesus conflict
- hemolytic - it is based on problems with the circulatory system. According to statistics, it occurs only in 1% of cases. The reason may be a different blood group for mother and baby and Rh factors. This type of jaundice may appear in the first hours of life and is instantly recognized;
- mechanical can occur no earlier than two weeks old. Occurs as a result of birth injuries or other genetic disorders. To provoke a mechanical jaundice can disrupt the biliary bladder;
- nuclear jaundice view. The circulatory system of a baby has a specific barrier that blocks the access of toxic substances to the brain. If the level of bilirubin is greatly increased, this barrier may not withstand the load, as a result of which nerve cells begin to break down. The child becomes lethargic, may refuse to eat, the cry becomes monotonous, and sometimes he even throws the head back;
- conjugation view results from poor liver function;
- hepatic type may appear as a result of the action of viruses on liver cells.
The following signs are characteristic of physiological jaundice:
- The skin and whites of the eyes become yellowish, sometimes even close to orange;
- Stool irregularities may occur.
With pathological jaundice, the symptoms are other:
- Skin color becomes more saturated;
- Bruises may appear;
- The disease goes on for periods, the color of the skin is constantly changing from pink to yellow and in reverse order;
- The baby refuses to eat and looks sluggish;
- Muscle tone increases;
- Urine dark color;
- The kid constantly is naughty or publishes a monotonous moan;
- Cal has no pronounced color;
- Heart rate is too slow;
- In rare cases, there is a stupor or coma.
Methods of treating jaundice in newborns
Depending on the reason for the appearance of jaundice, the following methods of its treatment can be identified:
- Light therapy, or as it is also called phototherapy. To date, this method is the most effective. If the degree of jaundice is high, then such therapy is carried out continuously. Mother give baby only for feeding. If the indicator is not high, then the child may be under the lamp only a few hours a day. Among the side effects of emit: a small burn of the skin, sunburn, lactose intolerance, hemolysis, hyperthermia;
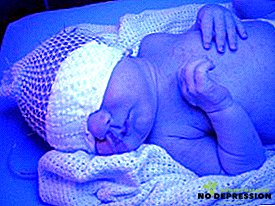
- Infusion therapy It is carried out in order to restore the body water balance during phototherapy. The solution is based on glucose with the addition of membrane stabilizers, soda, electrolytes and other components;
- In order to stop the circulation of bilirubin between organs such as the intestines and the liver, enterosorbents can be administered. This method is not used for self-treatment, it serves more as an addition to the main treatment;
- If there is a threat of nuclear jaundice, you can prescribe a blood transfusion;
- If the place has cholestasis, then you must use the drug Ursofalk. This medicine is not contraindicated for babies, as it is available in suspension;
- There are cases that for the treatment of jaundice you need to replenish the body with such vitamins as E, A, K, D3, zinc or calcium;
- If the newborn has problems with metabolism, then you need to resort to conservative methods of treatment. Preparations are prescribed taking into account the intolerance of certain elements by the child's body.
Zheltushka in newborns: consequences
So, as we have already found out, the physiological jaundice does not bear any harm to the baby. This is the usual reaction of the body of the baby to the world.
If jaundice is pathological, then the picture may be quite different. It is subject to compulsory treatment, and if this moment is ignored, its development is fraught with the following consequences:
- Zheltushka can cause toxic poisoning of the body. The fact is that bilirubin begins to accumulate in the fatty tissues, in the brain nuclei and the membranes of the nervous paths, which negatively affects the baby’s body;
- As a result of an excess of bilirubin, bilirubin encephalopathy may occur;
- At a later age, failure in neuropsychic development may occur;
- Another effect can be albuminemia;
- Due to nuclear jaundice, deafness and seizures may develop;
- Oligophrenia.
Any of the consequences depends on the type of jaundice. After all, each case is characterized by special symptoms and treatment.
In order to avoid any changes in the body, you need not to bring it to a neglected state and start medical intervention in time.
And some more information from Dr. Komarovsky about the jaundice of newborns - in the next video.