Polycystic ovary is a fairly common pathology in women. May occur due to various reasons and lead to infertility. A characteristic feature is that in the early stages the disease proceeds without obvious signs. In order to start treatment in time, it is necessary to know what polycystic ovary is, its symptoms and causes.
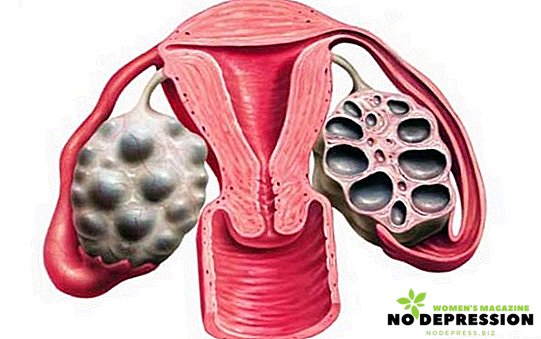
The main types of polycystic
At the moment, there are two forms of this pathology:
- Primary polycystic. It occurs in younger girls during the period of stabilization of the menstrual cycle. Another term is sclerocytosis. This form is worse to treat, often caused by a hereditary factor, but surgery can help.
- Secondary polycystic. Observed and developed after the establishment of the monthly cycle or after the birth of the child. It usually occurs as a result of inflammation of the reproductive organs or the development of endocrine diseases, and is most often observed in patients with obesity or an excess of insulin in the blood. May occur during menopause. This form is more amenable to treatment.
At the moment, many experts argue that the appearance of polycystosis of both ovaries is possible, since the cause of this condition is a system failure.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of polycystic may be of varying severity. In some patients, there are separate manifestations that are associated with specific causes of polycystic. At the moment, the following symptoms are distinguished:
 Failure of the menstrual cycle due to disruption of the ovulation process. Monthly with this pathology are irregular or absent, the interval between cycles can reach 35 days or more, bleeding is recorded less than 8 times a year. Often, the long delay of menstruation is replaced by profuse prolonged bleeding due to the pathological thickening of the inner lining of the uterus.
Failure of the menstrual cycle due to disruption of the ovulation process. Monthly with this pathology are irregular or absent, the interval between cycles can reach 35 days or more, bleeding is recorded less than 8 times a year. Often, the long delay of menstruation is replaced by profuse prolonged bleeding due to the pathological thickening of the inner lining of the uterus.- Pain in the lower abdomen, periodically pulling, giving to the lower back or sacrum.
- The appearance of stretch marks on the skin of the chest, thighs, abdomen.
- Increased fragility of the nails and hair.
- Extra pounds - if the weight increases by about 10-15 kg. In this case, fat deposits are distributed either evenly or in the abdomen and shoulder girdle.
- Frequent relapses of thrush, pustular skin infections.
- Constantly increased temperature throughout the full cycle.
- Inability to conceive a child. Thus, with this pathology as a result of disruption of ovulation processes, primary infertility is observed in more than 25% of patients.
- Excess male hormones - androgens, which lead to the appearance of external male signs. These include: active hair growth on the face, abdomen, thighs, alopecia or hair loss, increased sebum production, acne.
Causes
At the moment, experts have not yet come to a common opinion about the causes of this syndrome, but at the same time, doctors believe that the disease is based on multiple disruption in the body:
- maturation of the dominant follicle;
- a disorder of the function of the pituitary and hypothalamus, which causes dysfunction of the ovaries and adrenal glands;
- violation of the production of androgens, increased production of melatonin and serotonin;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- failure of the genitals, which leads to a lack of ovulation.
Among the causes of polycystic disease, an abnormally active insulin production and low cell sensitivity to it are isolated. The insulin level becomes so high that the ovaries respond to this activity by producing male hormones. Overweight is another reason.
The reason may be heredity. Most often, the woman suffers from this pathology if her close relatives have had a history of a tumor of the uterus or genital organs. In addition, according to doctors, infectious diseases can trigger hormonal disorders.
Also lead to polycystic:
- emotional distress;
- poisoning with chlorine, benzene, phenol;
- long-term use of birth control pills.
Consequences of polycystic
The consequences of this disease with a long course and without therapy may be as follows:
- In 50% of cases, a woman is not capable of conception, has frequent miscarriages.
- Severe anemia due to massive bleeding.
- Disturbances in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, which initiates the gradual development of diabetes mellitus, which is diagnosed in 50% of patients by the menopause period.
- Gestational diabetes or preeclampsia can develop during pregnancy.
- The risk of developing atherosclerosis, heart disease, stroke increases due to the elevated testosterone levels.
- Malignancy or malignant degeneration of endometrial cells, which is provoked by excessive growth of the endometrium as a result of the absence of menstrual bleeding or due to elevated levels of estrogen.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis is an important step, allows us to distinguish this disease from other pathologies with similar symptoms, to choose the right therapy strategy, since the treatment methods depend on the reasons that caused this syndrome.
To make an accurate diagnosis requires a complete examination, which includes ultrasound and laboratory tests.
To determine polycystic on ultrasound in order to accurately diagnose it is carried out three times during the month. A single ultrasound scan is not enough to make a diagnosis.
Symptoms of polycystic:
- multiple follicular cysts are located under the thickened capsule and on the surface of the ovary;
- The ovaries can grow up to 4 cm wide and up to 6 cm long;
- endometrium thickens;
- Often there is a decrease in the volume of the uterus itself.

It is very important to donate blood to study the level of hormones, sugar, lipids in the blood. Do the analysis of such hormones as:
- Androgen adrenal glands. For proper treatment, it is necessary to establish what caused the excessive production of male hormones. This indicator is required to identify internal causes.
- Free testosterone. If free testosterone in the blood is more than 1%, women will definitely show signs of hyperandrogenism.
- FSH and LH. This analysis is needed to identify abnormalities in the pituitary gland. If LH is more than normal, and the ratio of LH and FSH is increased, this indicates the presence of disorders of the pituitary gland in the regulation of the reproductive system.
- Estradiol. It is the most active estrogen. Its reduction or increase indicates the presence of a problem.
- Cortisol. Deviation from the norm indicates severe stress, which can trigger the development of preeclampsia.
- Prolactin. It is a hormone that makes the pituitary gland. Elevated levels of prolactin often indicate a pituitary tumor, which, in turn, leads to excessive hormone production. In addition, the high content of prolactin inhibits the ability to conceive. Its increase may indicate such causes as a tumor of the hypothalamus, pituitary, Cushing's syndrome.
When polycystic, depending on the causes in the blood plasma can be observed:
- an increase in LH of more than 2.5 times;
- lowering of FSH;
- increased estradiol levels;
- increase in the content of free testosterone and prolactin.
Analysis of hormones should be carried out in certain phases of the menstrual cycle, otherwise, these studies will be uninformative. Thus, the analysis for LH, FSH, prolactin should be taken on the 4-5 day of the monthly cycle, on free testosterone - on the eighth day, on progesterone and estradiol - on the 21st day of the cycle. If the phases were not expressed, blood must be re-tested after 10 days.
For complex diagnostics, the following types of additional studies are carried out:
- determination of lipoprotein concentration;
- test for glucose tolerance, because elevated insulin levels indicate a violation of carbohydrate metabolism;
- tests for thyroxin, thyrotropin.
Laparoscopy may be performed for differential diagnosis. Usually, in the course of this procedure, enlarged ovaries are determined, their surface is examined (most often it is hilly, follicular capsules have a characteristic white color). In addition, laparoscopy in this pathology is one of the most effective and gentle methods of surgical treatment of this pathology.
Features of treatment of polycystic ovary
Since this pathology is most often accompanied by unstable insulin resistance, polycystic cures with replacement therapy are treated. Self-treatment is strictly prohibited.
Preparations
To restore the function of the pituitary and hypothalamus, it is necessary to use oral contraceptives with antiandrogenic properties. Duration of treatment - 2-3 months in the absence of pregnancy planning. The most famous drugs - Janine, Regulon.
It is also necessary to use drugs from other pharmacological groups:
- To stimulate ovulation, if you want to become pregnant, for example, Duphaston or Utrogestan. Hormonal tablets are taken according to a specific pattern for a course of 4 months.
- Antiandrogens that help block male hormones are Veroshpiron, Flutamide. Take up to 3 pills per day.
- Drugs that are needed to increase insulin sensitivity - Glucophage, Bagomed.
Operation
If there is no positive trend in drug treatment for a year, doctors prescribe surgery. Currently, the most well-known methods of treatment are laparoscopy, wedge resection, electrocoagulation.
Diet
An important point in polycystic ovaries is diet. Thus, the caloric content of food should not exceed 2000 calories, while you need to eat up to 6 times a day in small portions. The amount of carbohydrates in this case should be 45% of the total volume of food, while the volume of proteins is not normalized. The ratio of animal and vegetable proteins is one to three.
With ovarian pathologies, the following products are allowed:
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- greenery;
- low-fat dairy products;
- low-fat varieties of fish and meat;
- mushrooms and cereals.
When polycystic prohibited the following products: fast food, sweets, potatoes, bakery products.
Traditional methods of treatment
It must be remembered that such therapy can only be ancillary and should be coordinated with the attending specialist. The most effective and widely available methods include:
- Take 80 g of pine forest uterus, pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave to infuse in a dark place for 2 weeks. Take the finished composition in half a teaspoon 3 times a day for a month.

- Take 100 grams of green peeled walnuts, add 0.8 kg of sugar, pour 0.8 liters of vodka. Insist for two weeks, take one teaspoon for 3 weeks.
- Broth nettle or milk thistle. It can be treated with this remedy for up to 4 weeks.
Polycystic and pregnancy
Infertility is recorded in more than 50% of women with this pathology. After correct treatment, 80% of patients manage to restore ovulation, but the effectiveness in terms of fertility is only 55-60%.
A woman with this diagnosis is faced with the main question - how to get pregnant with polycystic disease, given the fact that this disease is the main factor in the development of infertility. Stimulation of ovulation in polycystic is carried out with the use of the drug Duphaston.
But pregnancy during illness often turns into complications such as bleeding, risks of early miscarriage, fetal dying. In this case, the doctor must prescribe:
- diet;
- hormone replacement therapy;
- laparoscopy.


 Failure of the menstrual cycle due to disruption of the ovulation process. Monthly with this pathology are irregular or absent, the interval between cycles can reach 35 days or more, bleeding is recorded less than 8 times a year. Often, the long delay of menstruation is replaced by profuse prolonged bleeding due to the pathological thickening of the inner lining of the uterus.
Failure of the menstrual cycle due to disruption of the ovulation process. Monthly with this pathology are irregular or absent, the interval between cycles can reach 35 days or more, bleeding is recorded less than 8 times a year. Often, the long delay of menstruation is replaced by profuse prolonged bleeding due to the pathological thickening of the inner lining of the uterus.











