Bilirubin is a substance that is formed in the human body due to the breakdown of red blood cells. To determine the rate of this element, it is necessary to pass a laboratory blood test.
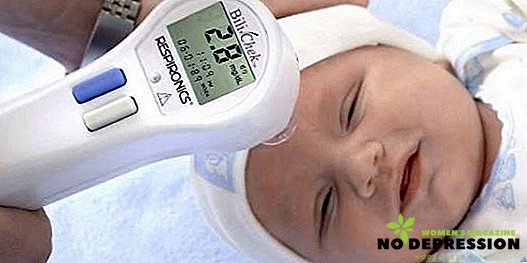
Without fail, blood is taken from newborns to exclude jaundice and its complications. If the indicators significantly exceed the permissible values, then it is recommended to carry out complex therapy.
Independent actions should be completely excluded, as this can lead to negative consequences for the baby.
Bilirubin and its importance for the newborn
Bilirubin can be direct and indirect. Direct view is not dangerous for the baby, because without complications excreted from the body along with bile, urine or feces.
The indirect appearance of this substance is considered toxic and also has a negative effect on the nervous system. It does not dissolve and is not excreted from the body, as a result, the child develops the corresponding symptoms - the skin and the mucous surface of the mouth immediately begin to turn yellow. To exclude such a deviation, the liver should function normally and facilitate the removal of this element from the body, using the intestines.

It must be remembered that bilirubin in a newborn is not capable of being fully and efficiently processed, therefore its content in the blood exceeds the norm to a great extent. It should be understood that this deviation is not always considered a pathology.
In the diagnosis, the age of the baby is necessarily taken into account, since the normal values are different. Therapy will be prescribed on the basis of the results obtained and only if the condition of the child does not stabilize over several days.
Norm bilirubin by day and month
Bilirubin is always present in the blood of a child, but in small quantities. After birth, the rate of this substance is determined in umbilical cord blood. The table below will show the bilirubin in the blood of a newborn depending on the day and month.
Norm bilirubin in newborns by day and month:
| Child's age | The amount of total bilirubin, µmol / l | The ratio of direct to indirect bilirubin
|
|---|---|---|
| At the newborn, in the first days | 50-60 | 90% to 10% |
| 2-7 days | Up to 256 | 90% to 10% |
| 7-14 days | 60-100 | |
| For 21 days | 8,5-20,5 | |
| The norm in a child aged 1-2 months | 8,5-20,5 | 75% to 25% (15.4 μmol / l at 5.1 μmol / l) |
The rate of direct bilirubin is 15-15.4 μmol / l, and that of indirect bilirubin is 5-5.1 μmol / l.
All the above data is considered normal only for full-term and term-born babies. As for indicators for premature, they are different.
 For these patients, bilirubin is considered to be more toxic, since the premature baby does not fully form the nervous system. For a child who was born ahead of time, the norm is not more than 172 µmol / l. The maximum value (limit) of this indicator is observed on the third or fourth day after birth.
For these patients, bilirubin is considered to be more toxic, since the premature baby does not fully form the nervous system. For a child who was born ahead of time, the norm is not more than 172 µmol / l. The maximum value (limit) of this indicator is observed on the third or fourth day after birth.
If, after the survey, there are significant deviations from the norm, then it is required to immediately determine the cause of the jaundice. In this situation, jaundice is not considered physiological, we can talk about the pathologies of the liver, impaired metabolism.
Causes, signs and consequences of deviations
Jaundice is physiological and pathological. The physiological type of this deviation is not considered dangerous for the child and does not indicate the development of any pathologies or diseases.
Appears at 2-4 days after the birth of a child and says that the children's organism adapts to the surrounding world. Yellowness of the skin disappears somewhere in 7-8 days, without any auxiliary measures. There are cases when physiological jaundice occurs in a child a week after birth.
Symptoms of physiological jaundice include the following symptoms:
- The appearance of yellowness for 2-4 days after birth.
- It takes a week or 10 days after birth.
- Skin color throughout the body can vary from orange to orange.
- The general condition of the baby is positive, there are no significant deviations.
- The behavior of the child is standard.
- Urine and feces are not changed in color.
As for pathological jaundice, it is considered dangerous for the child. To get rid of it will require complex therapy, which involves the identification and elimination of the cause. It occurs as a result of such provoking factors:
- rhesus-conflict mother and baby;
- premature birth;
- inherited diseases and pathologies, as well as genetic abnormalities;
- transferred infectious diseases of the mother during gestation;
- stimulate childbirth.

Symptoms of this type of jaundice are as follows: low blood pressure, cramps in the limbs, poor appetite, increased weakness and drowsiness, pronounced skin color, yellowness disappears first, and then gradually returns.
The danger of pathological jaundice is that at high levels of bilirubin, the enzyme can penetrate into the nervous system and harm it. In this situation, bilirubin encephalopathy is diagnosed in a small patient on the first day after birth, which leads to brain intoxication.
It is considered very dangerous and can lead to disability, and sometimes - to death. In this case, the corresponding symptoms will be present.
If the newborn is not given timely help with elevated bilirubin in the blood, then after 6 months he will have problems with hearing, development, and even partial paralysis will occur.
It is also worth to be wary and mom, be sure to pay attention to the color of urine and feces. When their color changes, it is necessary to examine the liver and gallbladder, as there is a possibility of developing the disease of the biliary tract and liver.
Treatment of elevated bilirubin
How to normalize the level of bilirubin in the blood of infants? The treatment is carried out comprehensively. If timely therapy is provided to the little patient, then yellowness disappears in 14-21 days and no consequences arise.
In any situation, treatment is prescribed exclusively by a specialist - pediatrician or neonatologist. Failure to take remedial actions can be dangerous. Yellowness must be constantly monitored, that is, laboratory blood tests should be conducted.

To normalize the condition of the child, you need to adhere to the following recommendations of a specialist:
- Using the lamp. It is considered the most effective way to treat jaundice. Due to exposure to bright light, the components of bilirubin in the skin begin to gradually deteriorate. The baby during the procedure should be naked, and special glasses should be worn. There is a child under the lamp for several hours, and sometimes for several days.
- Reception of preparations. It is recommended to use such medicines as: Elkar, Smekta, Ursofalk, Hepel and others. They help to normalize the performance of the liver and gallbladder, eliminate intoxication of the body and destroy bilirubin.
Drugs are recommended to be taken from the first days of life. Available in the form of drops or suspensions. The dosage and course of treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
Preventive actions
To reduce the risk of jaundice in a newborn, it is worth carrying out preventive measures. What prevention of jaundice is provided for babies? In the period of gestation, it is necessary to pay attention to proper and balanced nutrition, to give up bad habits and taking medications that can harm a child.
It is recommended to breastfeed after birth. Try to eliminate constipation in the baby.
Elevated bilirubin in the newborn is not considered normal, but does not always indicate a deviation. Any violations are accompanied by severe symptoms and occur as a result of many provoking factors.
If necessary, complex therapy is required. To eliminate complications, it is necessary to adhere to the recommendations of a specialist.
Additional information about neonatal jaundice of newborns is in the following video.