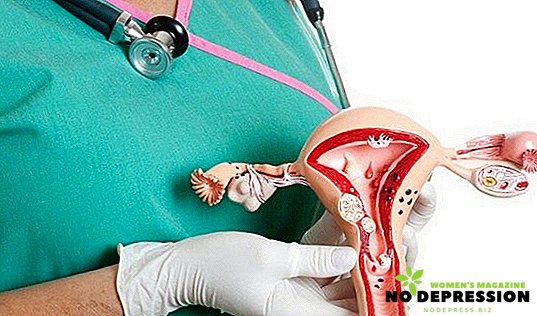
A cervical biopsy is a surgical procedure in which a piece of tissue is taken from the vaginal part of an organ for further examination. Such a procedure is often prescribed after the pathologies are detected during a gynecological examination, and the results of the tests will help to determine how the woman suffers from the disease.
What is a biopsy prescribed for and what does it reveal
Basically, this procedure is prescribed after the discovery of pathologies in the cervix. Most often this happens when signs of cancer, precancerous conditions, and papillomavirus are detected.
This procedure will allow you to investigate the structure of the cells of the cervix uteri, to determine the signs of diseases.
The obtained histological conclusion will allow the specialist to correctly diagnose, determine the prognosis of the disease and prescribe an effective treatment.
Also, cervical biopsy is used to confirm the diagnosis.
Cases of appointment procedure
A biopsy is prescribed after a colposcopy, if during the procedure were found:
 white areas, which are formed after treatment with acetic acid. Most likely, it speaks of dysplasia;
white areas, which are formed after treatment with acetic acid. Most likely, it speaks of dysplasia;- areas that have not changed shade after treatment with iodine - this indicates a change in tissue. This, for example, is observed in uterine leukoplakia;
- red spots, which may be associated with the growth of blood vessels;
- mosaic of branched papillae, which are divided into small vessels;
- bumpy and nervous surface that may indicate cancer;
- condyloma or atrophy, inflammation.
Varieties and Characteristics
There are the following types of biopsy:
- Puncture, in which they take a small piece of tissue with the use of special forceps.
- Wedge-shaped. In this case, the cone-shaped section of the neck is removed using a laser beam or scalpel. A biopsy is performed under general anesthesia.
- Scraping the cervical canal - removal of cells from the canal using a curette.
The choice of the appropriate method depends on the disease, the degree of development, the patient's condition.
Proper preparation for cervical biopsy
The procedure depends on the menstrual cycle. It is usually prescribed a week after the first day of menstruation. Due to this, the wound that appeared during the procedure will have time to drag on to the next cycle, which will reduce the risk of the development of the inflammatory process. Also, this will prevent endometrial cells from getting into the wound and, accordingly, the occurrence of endometriosis.
As preparation, prescribe such survey methods as:
- urine and blood tests;
- determination of the level of bilirubin, sugar, urea;
- coagulogram - blood coagulation test;
- smear on the microflora;
- testing for syphilis, hepatitis, HIV;
- colposcopy.
When an infectious process is detected, a biopsy is prescribed only after the elimination of the disease.
You also need to tell your doctor about the drugs taken, because there are drugs that can increase the risk of bleeding. These include Aspirin and Ibuprofen.
The specialist also needs to report on:
- the presence of allergies to medications;
- recurrent bleeding in the patient or family members;
- the presence of diabetes, heart disease;
- previous surgical interventions, for example, the removal of the appendix.
 A day before taking a biopsy, you need to douch, do not use special ointments, creams, candles.
A day before taking a biopsy, you need to douch, do not use special ointments, creams, candles.
Before the procedure you should not take alcoholic beverages, use any means for intimate hygiene. If the patient suffers from diabetes, you need to consult a doctor in advance. Also, before the biopsy you need to visit a gynecologist.
After consultation with the doctor, the woman signs consent to the procedure.
If anesthesia is planned during the taking of the material, then in 12 hours it is necessary to refuse to take food, any liquid and medicines. After the operation, the woman may open a little bleeding. Therefore, the procedure itself must take gaskets. Also, after a biopsy, the patient will have a feeling of drowsiness, so the accompanying person should be with her.
Procedure Procedure
Depending on the volume of tissue to be removed, a biopsy can be performed both in the clinic under local anesthesia, and in the hospital under general anesthesia. The procedure itself begins with an examination by a gynecologist. Next, anesthesia is done: either irrigation of the cervix with a special spray with lidocaine, or its introduction into the tissue.
When the drug acts, a dilator is inserted into the vagina, the neck is grasped with forceps and gently lowered closer to the entrance, treating with iodine to determine suspicious areas. Further, using a special tool, pathological tissue is removed.
If there are several pathological areas, the doctor will take several samples. Moreover, a piece of tissue should be no less than 5 mm in width and depth, which will determine the extent of the pathological process in healthy cells.
A tool such as a conchotome can damage tissue, which later will make it difficult to study the material. Diathermy biopsy can lead to charring of the edges of the tissue, which will also reduce the quality of the material under study. It is best to carry out the procedure for taking a biopsy using radio waves: a special device is used that allows you to "pinch" healthy tissue as quickly as possible and without blood.

After that, stitches are placed on the wound, which will subsequently dissolve. When carrying out a knife biopsy, a special sponge soaked in aminocaproic acid is inserted into the vagina, this is required to stop the bleeding. But when conducting radio wave methods, such preparatory manipulations are not required, since the heat radiated from the device “seals” the damaged vessels.
After receiving a tissue sample, it is immersed in a formaldehyde solution and sent to the study.
Recovery after taking the analysis
When performing an excision biopsy, which is performed on an outpatient basis, the patient can go home immediately after the procedure. Hospital discharge for several days. If, however, it was decided to conduct a konization, then the woman should be under the supervision of a doctor for two more days, the sick-list is issued for 10 days.
In the first few days, small pains, bloody discharges may disturb. If you have been treated with green paint, the selection may have a green tint. It is considered normal if the symptoms persist for seven days. If pain causes discomfort, you can drink any painkiller. As a preventive measure of infectious complications, medications can be prescribed, for example, Terzhinan suppositories.
You may also prescribe such medications:
- antimicrobials such as metronidazole;
- candles Genferon to enhance immunity;
- suppositories that accelerate wound healing.

In the period after the operation, it is recommended to wear underwear made from natural fabrics, to use daily pads. Daily hygiene procedures should be carried out with odorless and fragrance-free soap.
After a biopsy is prohibited:
- lift weights more than 3 kg;
- use tampons;
- conduct douching procedures for 10 days;
- have sexual intercourse within 4-6 weeks after a biopsy;
- take a bath or go to the swimming pool for 3 weeks.
Interpretation of biopsy results
According to the results of the study of the material obtained, the specialist will be able to determine whether there are altered cells in the organ. Such violations can either not threaten the health, or be signs of serious diseases.
You can identify multiple groups of changes.
Background. Such changes do not go to the stage of cancer, but can provoke the development of the following diseases:
- dishormonal, for example polyps, leukoplakia, papilloma;
- inflammatory, for example cervicitis;
- posttraumatic, which include rupture of the neck, scars.
Precancerous. Such diseases are not malignant, but with a probability of 50% can develop into a tumor. These include:
- the appearance of dysplasia;
- adenomatosis.
Reviews
My gynecologist at the clinic issued a referral for a biopsy, because she didn’t like my tests, I had to clarify the diagnosis. She decided to do it for a fee, but did not choose a doctor, but went to the nearest clinic near the house. This was my mistake, because it was very difficult after it: there was a lot of blood, there was dizziness, although the procedure itself was quite painless. Pleases only one: no bad diagnoses were not confirmed. My advice - look for a good doctor!
Anna, 41 years old
After suffering the disease, a biopsy had to be done: I had been reading a lot of negative reviews about this operation, I was terribly afraid, I spent a lot of time trying to find a normal clinic, a doctor. Spent two weeks on it. It was very scary, but everything went pretty well: it didn't hurt, there was only a little bit of blood after the biopsy, so everything went well.
Irina, 38 years old
Depending on the detected changes, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. It is for this reason that biopsy is an indispensable method for detecting a disease.


 white areas, which are formed after treatment with acetic acid. Most likely, it speaks of dysplasia;
white areas, which are formed after treatment with acetic acid. Most likely, it speaks of dysplasia;