This pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, like peptic ulcer, has a clear relationship with Helicobacter pylori. How does this bacterium affect the development of gastritis and ulcers? What to do if you have Helicobacter pylori?
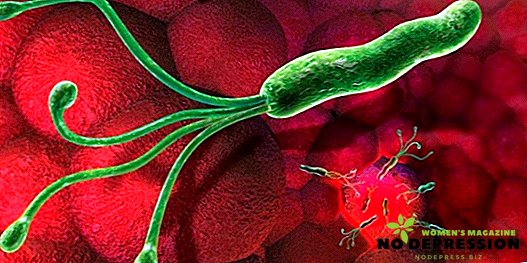
What is Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a human pathogen that is one of the causes of peptic ulcer. This bacterium is unique due to its survival in the aggressive environment of the stomach.
The ability to be fixed and held in the mucous membrane, Helicobacter owes its shape in the form of a spiral and the presence of flagella.
What is the danger of infection?
The environment in the stomach is normal acidic due to the production of hydrochloric acid.
Helicobacter pylori has an enzyme such as urease. Urease promotes the formation of ammonia by cleaving urea. Ammonia, in turn, neutralizes hydrochloric acid. Reducing the concentration of the latter leads to a local increase in the pH of the stomach to 6-7, which is optimal for the life of the bacteria.
Due to the constant neutralization of hydrochloric acid with ammonia, the cells of the stomach and intestines become inflamed and then die.
How can you get infected
The most common route of transmission is a contact-household with oral mechanism.
The spread of Helicobacter pylori occurs usually among crowded people who use the same dish when kissing. The mother can infect the child through saliva (on the nipple, cutlery). Therefore, therapeutic measures should be carried out among all family members.
It should be noted that in the environment the microbe is unstable (quickly dies).
Also, Helicobacter can be infected through insufficiently processed medical instruments during FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). This route of transmission is called iatrogenic, is rare.
Main symptoms of helicobacteriosis
Most people infected with Helicobacter are not even aware of this, since it does not manifest for a long time. In the presence of adverse factors from a latent clinical form, helikobacteriosis can pass into another.
Helicobacter pylori can occur in the form of acute and chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis and peptic ulcer.
Signs of acute gastritis include high intensity pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting. In the event that proper treatment has not been carried out, acute gastritis becomes chronic.
Chronic gastritis is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. In the first case, the person is disturbed by the same symptoms as in the acute form of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. In the period of remission, heartburn, bad breath can disturb.

With gastroduodenitis, pathological changes affect not only the stomach, but also the duodenum. The above-mentioned complaints characteristic of gastritis, joins disorder stool (constipation or diarrhea).
The development of gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer is one of the most serious consequences of helicobacteriosis. An ulcer is the presence of a defect in the mucous membrane. Pathology has a clear seasonality (autumn-spring) and the relationship with food intake.
For defects of the gastric mucosa is characterized by the so-called "early pain", which occurs thirty to sixty minutes after eating. In case of duodenal ulcer, a person notes pain syndrome on an “empty stomach”, especially at night.
Pathology such as peptic ulcer is dangerous for its complications, which can be life threatening. Complications include:
- bleeding;
- penetration (spread of the disease to nearby organs);
- malignant rebirth;
- perforation (through defect in the organ wall);
- stenosis (narrowing).
Diagnostics
Helicobacter pylori search is performed using invasive and non-invasive diagnostic methods.
Their difference is that in the first case endoscopic examination is required, and in the second there is no.
Invasive methods
With an invasive method, the doctor examines the stomach and duodenum with an optical device, and then takes a biopsy (a piece of tissue) from the most suspicious areas for histological examination. Also, the resulting biopsy can be subjected to bacteriological, PCR studies and tests for the determination of urease.
Bacteriological examination is a culture of culture media followed by determination of sensitivity to antibiotics if growth of colonies of microorganisms has been observed.

PCR refers to the molecular diagnostic method, in this case, the search for the DNA of bacteria.
Detect urease (Helicobacter pylori enzyme) allows the test with urea. In connection with the breakdown of urea, the pH changes. This change is fixed by the indicator. So, for the urease test, you need to place a biopsy in a solution with urea and an indicator. In the presence of helicobacteriosis, the color of the solution changes.
Non-invasive methods
Divided into immunological (search for antigen or antibodies) and biochemical.
If a bacterial antigen is searched, then feces are used as research material. The method is highly efficient. It can be widely used in children or in case of refusal to perform gastroscopy.
The biochemical method of non-invasive research is carried out using a respiratory urease test. The presence of Helibacter pylori is determined by exhaled air. The study must be done in the morning on an empty stomach. This method is used both to control eradication and to detect Helicobacter.
Treatment of the disease
Helicobacter pylori is subject to eradication (removal) with several drugs. The use of several pharmacological agents is necessary due to the lack of effectiveness of one of them.
Developed several schemes of therapeutic effects on the bacterium. Treatment can be carried out using three or four drugs.
Practically all treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori include drugs that block the proton pump.
The mechanism of their action is aimed at reducing the production of hydrochloric acid, increasing the effectiveness of other drugs. The drug is taken in the standard dose.
The composition of eradication schemes Helicobacter pylori necessarily include antibacterial drugs. Due to the growing resistance of the bacteria, it is proposed to take at least two antibiotics.
Most often it is clarithromycin and amoxicillin. The first is used in the dosage of five hundred mg twice a day, the second - a thousand mg twice a day. Metronidazole can be used instead of amoxicillin at a dosage of 500 mg twice a day.

After the eradication, it is necessary to check its effectiveness. The control study is most often carried out by a non-invasive biochemical method (breath test), so it is quite reliable and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
When is the control carried out?
After completing the course of treatment, four to six weeks should pass. During this period, it is prohibited to take any antibiotics.
What to do if the treatment was ineffective?
In this case, a second course of eradication is prescribed, but already using four drugs. Second line therapies include:
- proton pump blocker (standard dose twice a day);
- bismuth-containing drugs (standard dose);
- metronidazole (one and a half grams per day);
- tetracycline (two grams per day).
The duration of medication depends on the individual indicators, which are determined by a specialist. Most often it is at least seven days.
Attention! After each course of anti-helicobacter therapy, it is necessary to undergo control.
Treatment of folk remedies
Among the folk remedies, an infusion consisting of flowers of pear, apple, strawberry, bilberry leaves is suggested. To prepare the infusion you need:
- take one tablespoon of all the plants listed above and pour one liter of boiling water over them;
- insist for thirty minutes and then strain.
Drink half a cup of infusion twice a day.

Also recommended the use of hypericum, yarrow, calendula.
Alcoholic propolis tincture is used as an antimicrobial agent (twenty drops three times a day for seven days).
Symptoms and features of the treatment of Helicobacter pylori in children
Young children are usually infected by the mother if she licks a spoon or nipple. Infection of schoolchildren and preschoolers also occurs in the family when using the same utensils, non-compliance with personal hygiene.
The course of helicobacteriosis in children, as in adults, often proceeds latently. Clinical manifestations are characterized by pain in the epigastrium (upper abdomen), heartburn, heaviness in the stomach, bloating, abnormal stool, weight loss and appetite.
Small children can not say what gives them discomfort, but you can notice they have a poor weight gain, upset stool and eating behavior.
It should be noted that complications of helicobacteriosis in children occur much faster than in adults. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in childhood presents certain difficulties due to the inability to use some antibacterial drugs.
The treatment regimen usually includes metronidazole or amoxicillin, clarithromycin, proton pump blockers. The course duration is seven days, after which it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of eradication.
Tetracycline is not used in children because of its high toxicity.
Diet for Helicobacter pylori
The main criterion, which is presented to food in the presence of helicobiosis, is to exclude irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract with food. It is best to eat dishes in a shabby form. Recommended fractional diet (every three hours).
Observe the optimum temperature of the food. It must be served warm. The diet should contain dairy products, low-fat soups, cereals, vegetables in the form of mashed potatoes, meat (stew), fish.
It is necessary to exclude alcoholic and carbonated drinks, fatty meats and fish, smoked meats, pickles, spicy and canned foods.
Prevention
Avoiding helicobacteriosis will help:
- personal hygiene;
- if you have small children, do not need to lick their nipples, cutlery;
- You should not try food and drinks from one spoon, a cup;
- examination and treatment of the whole family, if one was diagnosed with helikobacteriosis.
Reviews
I am 24 years old. For about sixteen years, pain in the upper abdomen and heartburn began to disturb. I decided to check. Made fibrogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy. After some time, a positive response came to Helicobacter pylori.
Seven days she took amoxicillin, clarithromycin and omeprazole, followed a diet. Five weeks later, I went to pass a control respiratory test, which showed that no helicobacter was left. She began to notice that pain in the abdomen and heartburn almost did not bother. The doctor advised all the same to adhere to a diet, but already less strict.
Irina, 24 years old, St. Petersburg
Six months ago, helikobacteriosis was delivered to my child, as helikobacter pylori was detected in feces. Before that, the child refused to eat, complained of abdominal pain. After successful treatment with antibiotics, the specialist recommended that the whole family be tested. I also found a Helicobacter pylori infection.
It was also necessary to undergo a course of eradication. I was treated according to the three-component scheme. A month later, in a control study, they found that the therapy was ineffective. Now I will be treated with four drugs.
Catherine, 36 years old, Kyshtym
A little more information about the insidious Helicobacter pylori bacterium is in the next video.