Cytomegalovirus is a widespread virus that belongs to the herpes group. Since it was discovered only in 1956, there are still serious discussions between scientists and its origin. However, we must remember that it can adversely affect health, because it is so important to start treatment on time.
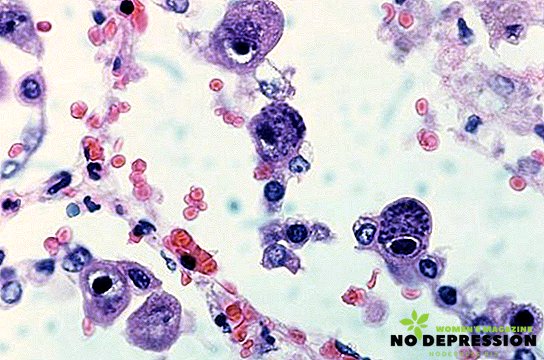
How is cytomegalovirus transmitted?
Cytomegalovirus is spread quite strongly; antibodies of this virus are found in 10-15% of adolescents and young people. In people aged 35 and over, it is found in 50% of cases. Cytomegalovirus is found in biological tissues - semen, saliva, urine, tears. When a virus enters the body, it does not disappear, but continues to live with its owner.
There are many ways of transmission of this virus, because its agents are present not only in the blood, but also in saliva, urine, semen, etc. For this reason, the possible transmission paths are as follows:
- airborne;
- with blood transfusions;
- during sexual intercourse;
- intrauterine infection.
It is also possible to transmit the virus during childbirth or breastfeeding.
It happens that the carrier of the virus is not even aware of its presence, especially in the absence of symptoms.
But if you overcool the body or reduce immunity, it can "wake up." Another factor that leads to virus activity is stressful situations.
What does it mean if cytomegalovirus antibodies are found in the blood?
IgM - antibodies, which our immune system begins to produce 3-6 weeks after infection. Antibodies of this type are also produced every time when the cytomegalovirus remaining in the human body after a previous infection begins to actively multiply again.
Thus, when an elevated level of antibodies is detected in the blood, this may mean the following:
- not so long ago there was a virus infection - during the last year;
- the virus has already been infected for a long time, but it is only now that the infection has begun to multiply.
 A positive IgM antibody titer can be stored in human blood for at least 4-12 months after infection. Over time, the antibodies disappear from the blood of a person infected with cytomegalovirus.
A positive IgM antibody titer can be stored in human blood for at least 4-12 months after infection. Over time, the antibodies disappear from the blood of a person infected with cytomegalovirus.
The incubation period is 20-60 days, the acute period is 2-6 weeks after the incubation period. Being in the body in a latent state both after infection and during periods of remission is unlimited time.
Even after undergoing a course of treatment, the virus in the body remains for life, the risk of recurrence remains, therefore, doctors cannot guarantee the safety of pregnancy even with the onset of persistent and prolonged remission.
The main symptoms
Even with normal and stable immunity, the virus can cause a mononucleosis-like syndrome. It usually occurs 3-8 weeks after infection and lasts for a month. Manifested in the form of fever, chills, cough, fatigue, malaise, there may be headaches.
Subsequently, the immune system is rebuilt, "preparing" to repel the attack on the body. But with a lack of strength, the acute phase can turn into a chronic one. It manifests itself in the form of a disorder of the vascular system, damage to internal organs.
In this case, the following manifestations are possible:
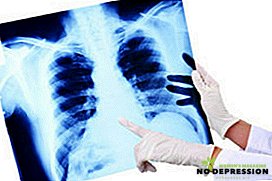 Generalized form. In this case, the virus affects some internal organs, which can lead to pneumonia, bronchitis, which will only worsen the situation by weakening the immune system. Treatment with antibiotics in this period may not be as effective as with ordinary bronchitis. At the same time, there may be a lesion of the vessels of the eyeball, a decrease in the number of platelets. External signs: skin rash, enlarged salivary glands.
Generalized form. In this case, the virus affects some internal organs, which can lead to pneumonia, bronchitis, which will only worsen the situation by weakening the immune system. Treatment with antibiotics in this period may not be as effective as with ordinary bronchitis. At the same time, there may be a lesion of the vessels of the eyeball, a decrease in the number of platelets. External signs: skin rash, enlarged salivary glands.- SARS. Manifested in the form of weakness, malaise, headaches, runny nose, fatigue, increased body temperature, the appearance of white spots on the tongue.
- The defeat of the genitourinary system. Usually manifested as an inflammatory process. But, as with bronchitis, inflammation is poorly amenable to treatment with antibiotics.
Particular attention should be paid to cytomegalovirus infection in the fetus, newborn child, young children.
Damage to the urogenital system manifests itself in the form of periodic and nonspecific inflammation. At the same time, as in the case of bronchitis and pneumonia, inflammations are poorly treatable with traditional antibiotics for this local disease.
Particular attention should be paid to CMV in the fetus (intrauterine cytomegalovirus infection), in the newborn and young children. An important factor is the gestational period of infection, as well as the fact whether the infection of the pregnant woman first occurred or whether the infection was reactivated - in the second case the probability of infection of the fetus and the development of severe complications is significantly lower.
In the case of infection of a pregnant woman, there may be such a problem as miscarriage due to the activity of the pathogenic agent. Also, the disease can lead to the death of the fetus (in 20% of cases) or to the appearance of problems with the central nervous system, brain in a child.
Infection during pregnancy: features
Most often, an infection in the period of carrying a child manifests itself in an acute form, in which the liver, lungs, and brain can be affected.
Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- fatigue, headache, general weakness;
- increased and sore when touched to the salivary glands;
- mucous discharge from the nose;
- abdominal pains that occur due to the increased tone of the uterus.
In children
Congenital disease is usually diagnosed in the first month of life. Symptoms include:
- cramps, trembling of limbs;
- sleepiness;
- visual impairment;
- problems with mental development.

Later manifestations are also possible when the child is over three years old. But in this case, the disease looks like a simple ARD, in which the following symptoms are observed:
- a slight increase in temperature;
- sore throat;
- runny nose
Diagnostic measures - how to detect the disease?
To diagnose this disease, you need to conduct a study of blood, smears, semen, urine.
So, first of all, prescribe laboratory tests that show the level of specific antibodies against cytomegalovirus - immunoglobulins M and G. They can indicate the presence of a primary or chronic disease.
Assigned to the method of PCR diagnostics, which will determine the DNA of the virus in the "fluids" of the body.
The diagnosis of a cytomegalovirus infection is based on the isolation of cytomegalovirus in clinical material or with a fourfold increase in antibody titer.
Moreover, such an analysis is strictly recommended to pass to pregnant women who usually have a cold, as this may indicate an infection.
Cytomegalovirus treatment
Treatment should be comprehensive, including all means that are aimed at combating the virus, and at improving and strengthening the immunity. At the moment, unfortunately, there is no medicine that will cure the virus forever - it remains in the body after therapy.
The main goal of treatment is to suppress the activity of cytomegalovirus. People who are its carriers should eat correctly and fully, give up bad habits, consume vitamins, useful trace elements.
But in most cases, the body can cope with the virus itself, and concomitant treatment is aimed at alleviating the symptoms.
So, to reduce the temperature, Paracetomol is usually taken, but Aspirin should not be used, because it has a lot of side effects. Also, do not forget about the correct lifestyle: fresh air, a balanced diet - everything that will strengthen the immune system.

You can also take immunomodulatory drugs - therapy can last several weeks. However, it is worth remembering that you need to take such funds only after consulting with a specialist.
Prevention rules - what needs to be considered?
Cytomegalovirus is the most dangerous in the period of primary infection, because it is so important to take all preventive measures, communicating with infected people. And such caution is especially important for pregnant women.
There are general rules to help you protect against a virus:
- do not have unprotected sex;
- use the same hygiene items, dishes;
- it is required to keep your house clean;
- wash your hands after a walk, contact with objects, money that have previously been in the hands of other people.
It is imperative to think about improving immunity so that even when the virus enters the body it does not become acute.
Possible consequences
In the case of a critical decrease in immunity, when the body cannot withstand viruses, cytomegalovirus infection becomes a generalized form.
This leads to inflammation and damage to internal organs:
- the kidneys;
- the liver;
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- CNS, etc.
According to WHO experts, this form of the virus today ranks second in the number of deaths after the flu.


 Generalized form. In this case, the virus affects some internal organs, which can lead to pneumonia, bronchitis, which will only worsen the situation by weakening the immune system. Treatment with antibiotics in this period may not be as effective as with ordinary bronchitis. At the same time, there may be a lesion of the vessels of the eyeball, a decrease in the number of platelets. External signs: skin rash, enlarged salivary glands.
Generalized form. In this case, the virus affects some internal organs, which can lead to pneumonia, bronchitis, which will only worsen the situation by weakening the immune system. Treatment with antibiotics in this period may not be as effective as with ordinary bronchitis. At the same time, there may be a lesion of the vessels of the eyeball, a decrease in the number of platelets. External signs: skin rash, enlarged salivary glands.









