Intestinal polyps are a dangerous disease that has a number of characteristic symptoms. Everyone needs to know them in order to consult a doctor in time and have a better chance of recovery. Symptoms of the appearance of polyps can vary in children and adults. Treatment is also selected according to age.
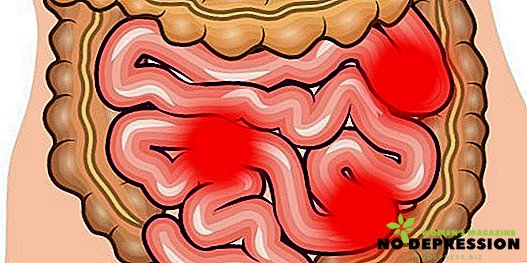
The essence of the disease, which are polyps
Polyps are called outgrowths formed by the intestinal mucosa. These formations are benign. They can be localized in the small or large intestine. This disease is called polyposis. It occurs in people of all ages.
In 1 in 10 people aged 40 years and over, there are neoplasms in the colon or rectum, and after 50 years in 1 out of 3 people.
More often the disease affects the male part of the population (about 1.5 times) than women. Timely diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of the disease leads to full recovery in 90% of cases.
Formations can occur singularly or multiplely and be arranged in groups (up to a third of all cases), as well as diffusely (familial polyps). Polyps, located in the colon, are localized on its broad basis (they are called "sedentary") or on the leg.
Polyps can be of several forms:
- branchy;
- spherical;
- mushroom.
Polyps differ in appearance. They are yellowish, reddish-gray, dark red, and may also have mucus on the surface.
In the form and structure of tumors are divided into several types:
- Inflammatory genesis (grow at the site of inflammation).
- Neoplastic (occur with the growth of atypical cellular structures).
- Hyperplastic (formed by overgrown normal cells).
By the nature of the growths produce benign and malignant.
Why do polyps form?
The appearance of polyps may be due to a lot of reasons. Scientists do not have a common opinion about the etiology of polyposis, so it is worth considering all possible options. Consider the main causes of the formation of polyps in the intestines.
Chronic intestinal inflammation
The inflammatory process localized in the intestinal wall can cause polyposis. This theory is the most popular and widespread.
The main evidence is that polyps do not appear on completely healthy tissues. There is a certain list of diseases contributing to the occurrence of polyposis:
- enteritis;
- typhoid infection;
- ulcerative colitis;
- dysentery;
- proctosigmoiditis.
As evidence of this list, the fact is that when recovering from these diseases, neoplasms in the intestines disappear. Also, the appearance of formations provoked by chronic constipation and intestinal dyskinesia.
Polypous growths occur in places most susceptible to stagnant fecal masses, especially when they injure the intestinal wall.
Deterioration of health on the background of adverse environmental conditions
Ecological distress affects all systems of human organs, including the digestive tract (gastrointestinal tract). These factors include unhealthy diet with an abundance of chemical components in the composition, which irritate the intestinal mucosa, as well as the lack of diet.
People are increasingly abandoning nutrition in favor of snacking on the go or at work. This affects the state of the digestive tract. The sedentary lifestyle, the lack of fresh air for breathing, and bad habits also have a considerable effect.

Vascular pathology of the digestive tract
In case of vascular pathology, the blood supply to the internal organs is disturbed, which has a negative effect on their condition. The pathological condition of the vessels of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract include:
- ischemia of intestinal tissues in atherosclerosis of the walls of the abdominal aorta, as well as its branches;
- varicose veins of the digestive organs;
- dyntricular disease;
- thrombotic lesion of mesenteric vessels.
Any of these conditions can trigger the development of polyposis.
Hereditary predisposition
In the case of the occurrence of polyps in children against the background of a healthy intestinal mucosa and if the child has relatives with polyposis, they speak of a family disease. It is believed that certain areas of the mucous contain abnormal genes that cause the appearance of tumors.
Food allergies
A particularly dangerous form of food allergy is considered gluten intolerance (celiac disease). Most often it affects children under one year. When such children eat gluten food, the intestinal mucosa is irritated, which causes polyps. Patients with celiac disease should be on a gluten-free diet in order not to provoke polyposis.

Often, when the causes are eliminated, the symptoms of polyposis disappear, and the existing polyps dissolve. Therefore, it is important to eliminate the causative factors in time when it is possible.
Do polyps turn into cancer?
Polyps are really able to move from benign tumors to malignant ones and cause intestinal cancer. It occurs in 10-30% of cases. Most often, the villous type of polyps, which resemble a carpet on the wall of the intestine, passes into a cancerous formation.
The incidence of polyp in cancer is higher in the hereditary form of the disease. Therefore, if the patient’s relatives have a polyposis, immediate surgical treatment is required.
Symptoms of polyposis
In many cases, this disease is asymptomatic in the initial stages. Polyposis has no pronounced specific symptoms.
It can be recognized by a combination of signs that are amplified in proportion to the increase in the size of polyps. Symptoms may vary depending on the type of polyp.
Symptoms and manifestations of polyps in the intestines in adults and children are as follows:
- Mucus and blood (including hidden) in the feces (inherent in villous adenomas).
- Chronic constipation, cramping pain, blood and mucus in the feces, as well as subjective sensations of finding a foreign body in the rectum and severe pain in the lower abdomen and iliac region are characteristic of large polyps.
- When a diagnosis of colorectal cancer is made, adenomatous polyps are found in 9 out of 10 cases.
- Dyspeptic disorders (diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, bloating) are characteristic of all types of polyps, since intestinal motility is impaired.
- Stagnation of feces most often occurs in neoplasms of large size.
- Pain in the area of intestinal projection indicates the beginning of inflammation in the background of polyposis.
- At infection of polypous formations paraproctitis occurs.
- Itching and discomfort in the lower part of the rectum occurs due to anal fissures, which appear due to constipation.
- Bleeding from the anus is the most formidable symptom that most often points to oncology, but may be due to rectal erosion.
If at least one of the symptoms is present, you should visit a general practitioner or a gastroenterologist who will prescribe an adequate examination. Early diagnosis of the disease leads to successful recovery, and in a neglected state, polyposis often leads to cancer.
Polyp diagnosis
The most common method of diagnosing polyposis is considered colonoscopy. The diagnosis is carried out by an endoscope, which is inserted into the anus and allows you to study the area of the intestine up to 1 m.
This procedure is considered mandatory for people from 50 years. For those who have relatives with colon cancer, a colonoscopy should be started annually much earlier.

In addition to colonoscopy, the patient may be prescribed other types of examinations:
- analysis of feces for the presence of blood, including hidden;
- irrigoscopy - the introduction of a contrast agent into the intestine with the help of an enema with further x-ray examination (it detects polyps more than 1 cm in the colon);
- digital examination through the anus (allows you to detect polyps in the lower part of the rectum, as well as erosive changes in its mucous membrane);
- rectoromanoscopy - a procedure performed by the endoscope and allowing you to view up to 30 cm of the intestine (this is a segment of the sigmoid colon and the whole line) and take material for biopsy (a piece of polyp tissue when it is detected to determine the nature of the neoplasm - benign or malignant);
- MRI and CT are the most advanced methods of research, allowing to determine the presence of polyps not only in the colon, but also in the small intestine.
Early and accurate diagnosis of polyposis is important because the disease is most successfully treated at the initial stage.
Treatment of polyposis in adults
This disease has no options for conservative treatment. Any detected polyp must be surgically removed followed by histological examination of the excised tissue.
If atypical (tumor) cells are found in the tissue, a decision is made to resect (remove) a segment of the intestine from which the test tumor was removed. The choice of tactics for the treatment of colon and small intestine polyps in adults is carried out depending on the location of the formation.

Transanal Polyp Removal
It is used when the polyp is located in the lower part of the rectum. To do this, use the hooks to expand the anal passage. The polyp itself is detected using an endoscope, and the removal is carried out with a loop electrode. In this case, the leg of the polyp is clamped with a loop of the electrode (electroscission).
Abdominal removal of polyps
Conducted with multiple polyposis, as well as in the presence of malignant polyposis formations. During surgery, the part of the intestine affected by the polyposis is removed. This method of treatment is used less frequently, as it is more difficult to carry out, and also has a longer recovery period.
After treatment, control colonoscopy is prescribed after 1 year, and then every 3 years. When new polyps are found, they are immediately removed.

Treatment of polyposis in a child
Polyps in children are treated only surgically, as in adults. Polyposis treatment in children is carried out not for the purpose of cancer prevention, but only to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and complications in the form of inflammations of the gastrointestinal tract, infection of polyps and bleeding.
Polyposis in children is treated by several methods:
- transanal excision;
- removal using an endoscope with an electric loop using electrocoagulation of the leg;
- polypectomy with colotomy;
- resection of the bowel area.
For each method of treatment there are a number of indications and contraindications. Sometimes methods combine with each other to achieve a better result.

Are there any folk remedies for polyps?
Since polyposis is not amenable to conservative treatment, there are no folk remedies for the correction of this condition.
But a certain diet and exclusion of provoking factors will help avoid the appearance of the disease, as well as new relapses. If you adhere to this lifestyle, then the polyps will not bother for a long time.
Polyposis prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance of polyps are necessary for all people over 50 years of age. This is a regular annual visit to the doctor for a colonoscopy or rectoromanoscopy.
Also, all people over 40 years old are recommended to regularly test for occult blood in the feces in order to notice and cure the disease in time without consequences for the patient.
It is also the prevention of cancer of the digestive tract.
Patient polyposis recommended a special diet. This diet is characterized by:
- the predominance of vegetable fats over animals;
- abundance of coarse fiber (beetroot, cabbage, zucchini, turnip, pumpkin, apples);
- restriction on alcohol use.
If you comply with preventive measures, then polyposis is highly likely to bypass the side. In the absence of preventive measures, the disease will progress and go into those stages when there will be practically nothing to be done.
Additional information about the disease considered in the article can be found in the following video.