A disease such as sialadenitis, occurs when salivary gland inflammation occurs. This problem occurs in children and adults, and can be caused both by an infection that has penetrated into the body, and also trivially due to poor hand hygiene. In our article we will look at what are the symptoms of this disease and how is the treatment.
Types and causes of sialadenitis
The cause of acute inflammation of the salivary glands is the presence of infection in the human body. Depending on the causative agent, sialadenitis is divided into the following types.
Viral
It develops with the appearance of the virus of mumps, that is, mumps, because the salivary glands are very sensitive to it. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. After entering the human body, the virus enters the gland, begins to multiply rapidly, which leads to inflammation.
If you do not start treatment in time, the infection in the boys is transmitted to the testicles, which can result in infertility.
Bacterial
Occurs when infection through the mouth or blood. In addition, oral microflora can cause acute inflammation of the salivary glands for the following reasons:
- Poor hygiene.
- Jet obturation, the appearance of which contributes to the operation in the abdominal cavity, as well as tumors, diseases that cause exhaustion of the body.
- Mechanical obturation, when the duct is blocked by a foreign object. In this case, active reproduction of bacteria begins inside the gland, which leads to inflammation.
- Infection through the blood usually occurs in the case of serious diseases such as scarlet fever, tonsillitis.
Chronic
In most cases, sialadenitis does not flow into the chronic form. Most often, this form of the disease occurs in poor immunity, heredity, and serious injury.
What symptoms will indicate inflammation
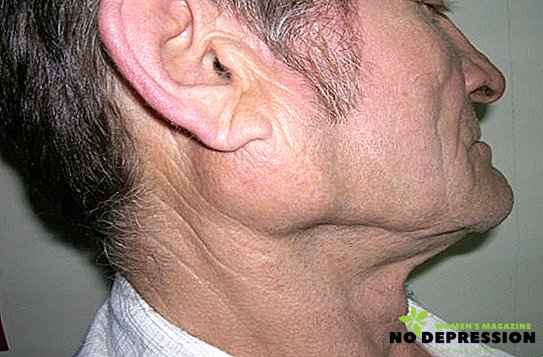
When inflammation of the salivary glands, the temperature rises, and the thermometer can show up to +39 degrees. In addition, the parotid areas swell, there is pain in the ears, jaw, especially when chewing.
 In acute inflammation, the symptoms depend on the location of the "lesion". Manifestations of acute inflammation in the absence of proper treatment are the following stages: serous, purulent, gangrenous.
In acute inflammation, the symptoms depend on the location of the "lesion". Manifestations of acute inflammation in the absence of proper treatment are the following stages: serous, purulent, gangrenous.
At the first stage, dry mouth appears, swelling around the ear. While eating, discomfort is only getting worse.
If the disease has flowed into a purulent form, the pain becomes sharper, sleep is disturbed, the body temperature rises to +38 degrees, it is difficult to open your mouth and chew. When probing the iron is dense, the skin around it is reddened.
But gangrenous sialadenitis can occur even without symptoms, but most often at this stage there is a sharp increase in temperature, the skin over the gland is destroyed, rejecting part of the dead gland.
In the absence of proper treatment, when the infection spreads through the body, the disease can cause death, so it’s important to consult a doctor in time.
But in a chronic inflammatory process, the symptoms are not so bright, which is associated with a slow course of pathological processes. During exacerbation, dry mouth is felt, the gland increases, it hurts when pressed.
How is the diagnosis and treatment of the inflammatory process
 To identify acute sialadenitis, the doctor must interview the patient and conduct a primary examination.
To identify acute sialadenitis, the doctor must interview the patient and conduct a primary examination.
A few years ago, a method such as sialography was often practiced, however, many doctors today are reluctant to refuse because of this method, the pathological process can be aggravated during the administration of a contrast agent, which intensifies the pain.
If there are symptoms characteristic of this disease, you should consult a doctor. Most often, inflammation is treated with conservative methods, and only at a purulent stage can an autopsy of the affected area be prescribed to remove pus.
Epidemic inflammation
In this case, doctors prescribe drugs to fight the infection, painkillers, drugs to lower the temperature, because in this case it is important to kill the infection so that it does not lead to inflammation of the glands.
Acute inflammation
The main goal of treatment in this case is the elimination of inflammation and the recovery of the glands. Most commonly prescribed:
- The use of antibiotics that are injected into the ducts. Penicillin or Gentamicin is usually used. They may also prescribe the use of antiseptics for removing pus.
- Use of compresses with Dimexide solution. They need to be done once a day for half an hour. This compress has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves pain, stops the growth of bacteria.
- Salivary diet. When it is necessary to use as much as possible crackers, cabbage, lemon, take orally 5 drops of hydrochloric acid pilocarpine. Due to this, there is a secret that contributes to the speedy recovery.

Also prescribed physiotherapy, antibiotics inside, special procaine blockade.
Surgical intervention
With the development of purulent inflammation will have to go under the surgeon's knife - the operation is simple and takes place very quickly, under general anesthesia. If the doctor finds a stone in the duct, it will have to be removed, otherwise the disease will reappear.
Chronic form
This disease is treated in the period of exacerbation by similar methods, as in acute inflammation. In addition, events such as:
- Massage ducts using antibiotics, which will remove pus and stop the growth of bacteria.
- Novocain blockade or electrophoresis during the month.
- Daily electroplating for 30 days.
- Introduction to the duct 5 ml of iodolipol (once every three months), which will reduce the risk of exacerbation.
- Reception of potassium iodide: three tablespoons three times a day. The course of treatment is at least a month.
- X-ray therapy, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, fights infection.
In extreme cases, an operation to remove the inflamed gland may be prescribed.
Traditional medicine in the fight against inflammation of the salivary glands
With this disease, many people practice using the methods of traditional medicine, but to avoid complications, you should consult with your doctor before using them.
Tinctures
 Hemlock tincture has an excellent anti-inflammatory effect - it is taken three times a day. On the first day you need to start with one drop of tincture 4 minutes before breakfast, then repeat the procedure at about 3-4 o'clock in the afternoon and in the evening about nine o'clock.
Hemlock tincture has an excellent anti-inflammatory effect - it is taken three times a day. On the first day you need to start with one drop of tincture 4 minutes before breakfast, then repeat the procedure at about 3-4 o'clock in the afternoon and in the evening about nine o'clock.
And continue this way every day, increasing the amount of tincture by 1 drop, until the total amount per day is 30 drops. Then start the countdown, daily cleaning one drop at the reception.
Also help and the following tincture, for the preparation of which we need:
- 300 g of celandine;
- 50 g of Hypericum;
- 50 g yarrow.
Mix all the ingredients, pour 700 ml of vodka, leave for a week in a dark room. After preparing the tincture of it you need to make compresses and apply to the sore spot.
Compresses
It is important to remember that such compresses can be used only in the absence of pus, otherwise they will only worsen the situation. The most effective recipes for compresses include:
- Cottage cheese. It is better to take a home, because it has more useful properties than in the store. Spread the product evenly on a gauze napkin and apply to the swollen area for an hour. And every day you need to take only the fresh product.
- Celandine. Pour 3 tablespoons of herbs 0.3 liters of boiling water. Put all ingredients in a saucepan, boil, and then leave for three hours. When the broth has cooled down a little, soak a piece of gauze in it and apply it to the diseased area.
Herbal Broths
Such broths help to stimulate the work of the salivary glands, thanks to this, the elimination of microbes and microorganisms is accelerated.
It is best to use herbs such as:
- Mint. It enhances salivary production, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Chamomile. Helps to remove puffiness.
- Raspberry leaves Promotes rapid healing of wounds.
With their help, you can make decoctions for oral administration or for rinsing.

For external use
The most well-known tools include:
- Camphor powder (20-30 g) mixed with 100 g of pork fat. Apply the resulting mass on gauze, attach to the damaged area, leaving for 2-3 hours.
- 1 tbsp. birch ash should be mixed with 3 tbsp. birch tar, lubricate the resulting inflamed area within three months.
- Take 40 g of Vaseline, 10 g of celandine, 10 ml of carrot juice. Mix all the ingredients and smear the swollen place three times a day.
Prevention Tips
To date, there is no special vaccine for this disease (there is only from epidemic mumps - it needs to be made to a child in one and a half years).
But there are several helpful recommendations that can help avoid infection:
- Do not forget about high-quality oral hygiene: brush your teeth, use rinsing. Make sure that children do not put their hands in their mouths on the street, because it is so very easy to get an infection.
- In case of common infectious diseases, do not forget about the oral cavity: rinse with furatsilina, a solution of potassium permanganate, thus avoiding the proliferation of bacteria.
As you can see, the inflammation of the salivary glands is not such a harmless disease, especially if we talk about boys, because in their case “mumps” can cause infertility. It is for this reason that it is so important to consult a doctor in time for the first symptoms.