The infant's body is subject to external adverse factors. Most mommies in the maternity hospital have to hear that their baby has bilirubin.
In order not to be afraid to hear these words, it is necessary to understand what bilirubin is (since not many people know this), as well as to know the causes of this phenomenon and the ways to solve this problem.
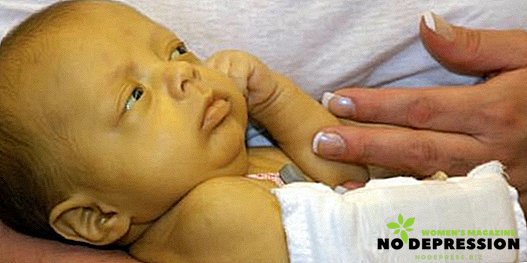
What is bilirubin, classification
Bilirubin is a pigment, the high content of which can give a poisoning effect to the nervous system of the baby. This pigment is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells in the blood.
In the course of their vital activity, red blood cells die off, as a result of which hemoglobin is released, as a result of which it becomes toxic to the child’s body. The immune system, in turn, begins to attack it, while releasing gems that contain iron. In consequence of gems and transformed into bilirubin.

Classification
In medical practice, there are two types of bilirubin:
- straight;
- indirect.
Direct bilirubin is eliminated from the body of the baby through feces and urine.
Indirect bilirubin initially connects with albumin and is transported to the liver, where after it is transformed into direct bilirubin.
Norm
The increase in bilirubin in the body of a baby in the first few days of life is a completely natural reaction. Therefore, in the maternity hospital, doctors often take a blood test to determine its level. If the pigment is significantly exceeded, then the baby has jaundice.
 In the first days of life, the level of bilirubin in the blood should be 60 µmol / l, after a few days the level of pigment rises to 205 µmol / l. and these are absolutely normal indicators and they absolutely should not frighten mom.
In the first days of life, the level of bilirubin in the blood should be 60 µmol / l, after a few days the level of pigment rises to 205 µmol / l. and these are absolutely normal indicators and they absolutely should not frighten mom.
If a child is born ahead of time, then the level of bilirubin in the blood is 170 µmol / l, but not more. When a baby turns 1 month old, the pigment level drops to 8.5-20.5 µmol / l.
If after 1 month of life the level does not fall and stays steadily at high rates, this may indicate the presence of various types of pathological changes in the body of the baby and in this case, the child shows hospitalization and additional laboratory tests that help identify and diagnose the disease.
Increased bilirubin in the blood of a newborn: what does this mean, causes
In medical practice, there are several main factors that caused an increased level of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn, however this applies only to those cases where a high level of pigment is kept in the blood for more than 1 month of life.
Pathological liver disease in a child. Symptoms in this case, in addition to increased bilirubin, are:
- Pain sensations. If we talk about newborns (who can not say about the pain), then they are often naughty, crying for no reason and pressing the legs to the stomach. Older children, who can tell about the nature of the pain, complain of pain in the right side of the abdomen under the ribs.
- Jaundice. Observed yellowing of the skin. However, since jaundice is quite common at birth, it is therefore necessary in this case to pay attention to symptoms of a different nature.
- Enlarged liver. This can be determined by examining the baby, namely, by palpation of the liver.
- Breaking stool A child with a disruption of the liver has regular liquid stools or alternating liquid stools with constipation.
- Change the color of the chair. In children with liver disease, the stool looks like clay, and is completely discolored (white).
Mechanical jaundice. It occurs due to blockage of the biliary tract.
Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis of the liver in infants is extremely rare, but if it is still diagnosed, the course of the disease will be much more progressive than in an adult.
Intestinal obstruction. Intestinal obstruction is a fairly common phenomenon among babies and close to 3% of babies suffer from it.
The first symptoms of obstruction are pain, the child often cries and presses the legs to the tummy, but in the early stages the disease can be confused with colic and only with time, if there are a number of other symptoms, is the obstruction detected.
Accompanying symptoms are: alternation of constipation and indigestion, after constipation begins to prevail, there is also bloating and flatulence. When running cases, the baby may experience vomiting with blood.

Medications. In some cases, an increase in bilirubin may be a consequence of taking certain medications. This can be observed in children whose mothers took medicines during pregnancy during the course of the disease.
Parents should be aware that the first 4 days of a baby’s life are one of the most important, since it is at this point that laboratory results can be used to determine if a child has pathological changes in time.
What is the danger of elevated bilirubin in newborns?
Increasing the level of bilirubin in the newborn for more than 1 month of life is extremely dangerous for the life of the baby.
If the level of pigment is much higher than its norm, at a time when it must return to normal, the bilirubin passes through the blood-brain barrier.
This phenomenon is extremely dangerous for the nervous system of the child. If you do not diagnose the disease in time, which entailed such consequences and do not begin to treat it, thereby lowering the level of pigment, then this threatens the child with dementia, as well as paralysis or hearing loss.
What tests need to pass?
- As soon as the baby was born, while still in the birth chamber, he measured the level of bilirubin in the blood. After two days, the analysis is repeated.
- In babies born early, the level of pigment is measured every other day, every day for several days.
- Blood sampling to determine the level of bilirubin in babies at risk (difficult pregnancy or childbirth, pronounced yellowness when born) blood is taken from the vein on the head, this process is repeated every day.
This procedure is absolutely painless, so moms do not have to worry about it, as the fence is carried out by an experienced doctor or nurse with a very thin and special needle.
 In children without pronounced symptoms of jaundice, blood is not taken for analysis, in this situation bilirubin is measured by a special device - bilitest. The procedure is absolutely painless.
In children without pronounced symptoms of jaundice, blood is not taken for analysis, in this situation bilirubin is measured by a special device - bilitest. The procedure is absolutely painless.
Bilitest is a device that measures the level of yellowness on the forehead of a baby, and the result can be seen instantly.
When the skin is yellow, the pigment level is measured throughout the treatment, until it drops to the optimal level.
The subsequent analysis of the baby is taken at the age of one month in the clinic, during the scheduled examination, blood is taken from the vein on the arm, however, some institutions practice the fence from the vein on the head.
How to reduce elevated bilirubin in newborns: treatment methods
With an increased level of pigment in the blood (for a long time), parents should immediately show the baby to a specialist who can make the appropriate diagnosis and as a result, prescribe treatment.
To remove bilirubin from the body of the baby using several techniques:
- Phototherapy This method consists in finding the baby under ultraviolet rays. For this child put in the crib, above which is the device. Getting ultraviolet on the skin of a child contributes to the removal of pigment from the body, but during this procedure, parents should be aware that such rays can harm the baby’s vision, therefore his eyes should be covered with a special bandage.
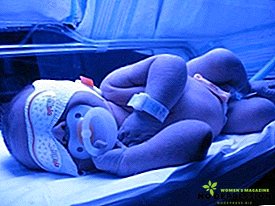
- Infusion therapy As a result of exposure to the skin of the child with ultraviolet light, a large amount of fluid is excreted from his body, and as a result, infusion therapy is prescribed, which helps restore the water balance in the baby’s body. To do this, glucose, soda, as well as microcirculation improving drugs are injected into the child’s body.
- Enterosorbents. In this case, is appointed Smekta or Entorosgel. This is necessary to prevent the reverse process of bilirubin absorption into the baby’s blood through the intestines.
- In severe cases, the baby is shown a blood transfusion.
The selection of methods for the removal of pigment from the body deals exclusively with the doctor.
When breastfeeding mom is recommended to more often put the baby to the breast, as this also contributes to the rapid removal of pigment from the body.
Consequences of elevated bilirubin in newborns
As mentioned earlier, significantly exceeded the level of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn, which lasts a long time, has a non-remediable effect on the nervous system of the child. What can then make an invalid out of a child (deafness, dementia), therefore it is so important to identify such a deviation in time and, as a result, to treat it.
Prevention
During pregnancy, the expectant mother should undergo all routine examinations and consultations with her attending gynecologist, take all necessary tests and in the presence of various infectious diseases in time to treat them.
Childbirth, if there are no contraindications, should take place in a natural way, using minimal medications.
One of the best preventive measures for removing bilirubin from the body of a baby is breastfeeding. Mom's milk has a laxative effect on the intestines of the baby, thereby the pigment will be quickly eliminated from the body.

Determining the level of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn is a very important study, so do not refuse, being in a maternity hospital or at a scheduled examination in the clinic from his. Since this analysis allows time to identify and prevent the occurrence of certain pathological diseases in the body of the baby.
A few more tips on the physiological jaundice of newborns can be found in the following video.