Chickenpox virus belongs to herpes viruses, and specifically to the group of herpes simplex. Children suffer this disease more easily and easily than adults, but they need to ensure proper treatment.
Infection process
Because children usually get chickenpox without complications at a young age, parents usually feel comfortable with contracting it. But a complete study of the virus and its activity in the human body has shown that not only the skin and nerve endings are affected, but also the internal organs, including the brain and even the fetus, if the woman is pregnant.
It is easy enough to infect chickenpox, because the virus is transmitted:

- Drops (talking, sneezing, coughing or kissing);
- Through close contact (contact with saliva or the contents of the patient's vesicles);
- In utero.
Since in public places it is fairly easy to contact closely (to talk or to be in the sneezing zone), you should be careful, especially in the spring-autumn period of exacerbation of the disease. Children from 4 to 6 years are extremely susceptible to the virus - up to 90% of the diseased.
There is also information about periodic epidemics of chickenpox, when it can affect a large number of people in one area in a short time.
Incubation period
The statistical incubation period for this disease is from 10 to 21 days.
The incubation period for chickenpox is longer in adults (16 days) and less in children (14 days) due to the nature of their immunity.
During the incubation period, the virus penetrates the respiratory tract, begins to multiply and accumulates in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The incubation period is divided into three stages:
- the beginning - infection and adaptation of the virus in the body;
- development - the virus multiplies and accumulates, the primary focus of infection is formed;
- completion - the virus spreads throughout the body, begins the production of antibodies.
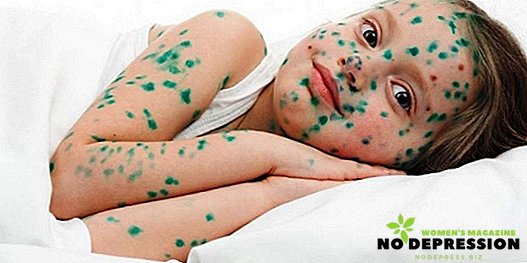
Symptoms of chickenpox in children
The onset of chicken pox is very similar to the development of a simple ARVI, so parents usually treat a child for a cold. But after the rash begins to appear and then you should see a doctor.

Chickenpox has the following symptoms:
- headache;
- poor appetite;
- general weakness;
- temperature from 37 to 38 ° C;
- rash for 1-2 days of illness.
The first rashes most often appear on the neck, on the border with the scalp and upper body. The subsequent rash spreads to the whole body, including the feet and palms.
The biggest problem with rashes is the itching they cause. Children begin to comb pimples, which can lead to scars afterwards.

Windmill forms
The weaker the immune system in humans, the harder it suffers as a strong infectious disease like chickenpox. Chickenpox has several forms of flow, conditionally, they can be divided into two forms: severe and mild, but the severe form causes complications and is divided into several subspecies:
- Light form - usually occurs in children from one to two to four years. That is why many parents are trying at this age to infect a child intentionally, allowing him to play with a carrier of the virus. It manifests a mild form only in the rash and slightly elevated temperature;
- Severe form - occurs in children from 5 to 12 years and older. This form is characterized by multiple skin lesions, large blisters and a rash in the mucous membranes. It is after severe form of chicken pox that acne scars can remain. The temperature in this form rises to 39.6 degrees and above;
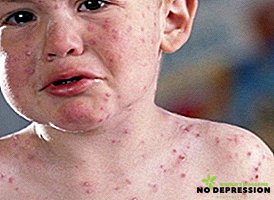
- The rudimentary form is complicated chickenpox, with no intoxication and temperature, but the rashes are abundant in the form of a roseolous rash;
- Pustular form - during this course of the disease intoxication begins and the temperature rises. The fluid in the blisters becomes turbid, with blood and pus;
- The bullous form - the only symptom of this form - is too large blisters on the skin. In addition, vesicles may appear and organism intoxication begins;
- The haemorrhagic form is the most complex form of chickenpox, occurring with complications. Inside the vesicles, hemorrhagic fluid accumulates, the skin is stricken with petechiae, bleeding and vomiting may begin;
- Gangrenous form - after hemorrhagic vesicles, the inflammatory process begins with purulent secretions, necrosis. Appears dystrophy and avitaminosis;
- The generalized form is often found in infants and can lead to the death of the baby. The rash affects not only the skin, but also the internal organs, leading to their necrosis.
Is the sick child contagious?
Chickenpox is an infectious disease, so every patient is an active distributor of the virus. Usually, the disease lasts for 21 days, but the child is considered infectious already three days before the first rash, and ceases to be infectious only five days after the appearance of the last pimple.
In general, a person is considered infectious for about 2 weeks.
Treatment of chickenpox in children
Treatment of chicken pox is carried out on an outpatient basis. Since chickenpox is an infectious disease, some wonderful medication has not yet been invented to treat it, in fact, the child simply needs to have it before an antibody to the pathogen is developed in his body.
The causative agent of the disease is a virus and it cannot be treated with an antibiotic. However, in the event of a bacterial infection (when the blisters begin to fester or when they are combed), antibiotics are also prescribed.

The main recommendations of doctors for the period of illness:
- comply with bed rest.
- change bed and underwear frequently;
- Do not wet the rash;
- lubricate the rash with a solution of manganese or brilliant green;
- follow a diet (dairy and vegetable products);
- drink plenty of fluids.
From the medication should be given to the child antipyretic tablets containing paracetamol in case of a temperature increase. Aspirin is strictly prohibited! As for other drugs, you can give:
- "Diazolin" to reduce itching, but only by prescription and in a safe dosage;
- "Fukortsin" to wipe the rash and dry them;
- "Acyclovir" antiviral drug to reduce the activity of the virus;
- "Miramistin" is an antibacterial drug that prevents bacterial infection of the vesicles.
All drugs prescribed for chickenpox, are aimed only at reducing itching from rash and preventing bacterial infection. As for Zelenka, it can also be used as a proven tool.
It dries pimples and has a disinfecting function. The best treatment for chickenpox is to spend time with your child, lie down together or do something, allowing him to simply recover and give the baby the body to cope with the virus, producing antibodies to it.
Possible complications
The most possible complication of chickenpox is the appearance of scars, which remain in place of the bubbles. This option is possible in two cases:
- the rash was severely combed;
- there was suppuration and inflammation of the vesicles.

The most serious and rare complication of chickenpox is inflammation of the brain (encephalomyelitis). Perhaps it is only in severe form of chickenpox and its complete ignoring, i.e. when a person was not given proper medical assistance and the virus hit the brain.
Congenital chickenpox, which is transmitted from a sick pregnant mother to her child, is also dangerous.
In most cases, varicella occurs in children older than 1 year without complications and leaves no consequences. Of course, subject to proper care and timely treatment.
Recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky is distinguished by a common view on the treatment of children and this is what he says about chickenpox:
"Viral infection, which is chickenpox is not treated with medicines, although in severe cases anti-herpes drugs are used. All that parents can do is alleviate the child's condition. Namely:
- Maintain a cool temperature in the baby’s room, because the warmth of the rash itches especially hard;
- the room must have moist air;
- the baby should drink a lot - do not force the child, but you should regularly offer him milk, tea or berry fruit juice;
- feed the child at his request, but reduce the overall caloric content of the food. Add more vegetables and fruits, dietary meat and fish. If the rash appeared on the mucous membrane of the mouth, then the child should be fed only with broths and soft mashed potatoes. All food should be at room temperature;
- change bed frequently and dress the child;
- You can bathe the child under a warm short shower, after which gently soak him with a towel.
As for the treatment, the main task is to relieve the itching of the rash and prevent the bacteria from penetrating into the vesicles, otherwise bacterial infection will begin.
Active rash and itching begins on the third day after the onset of the disease. The bubbles begin to accumulate fluid, while the body temperature may rise sharply. Paracetamol or ibuprofen can be used in age appropriate dosages. Aspirin can not be used in any case!
 Good for itching lotions with zinc oxide or with panthenol. Zelenka can also be used, but it is less effective in modern disinfecting solutions, it is simply very convenient to note the appearance of a new rash. Antihistamines are also used by the decision of the attending physician.
Good for itching lotions with zinc oxide or with panthenol. Zelenka can also be used, but it is less effective in modern disinfecting solutions, it is simply very convenient to note the appearance of a new rash. Antihistamines are also used by the decision of the attending physician.
The most difficult days of chickenpox are the first 3-6 days, after which the rash stops, the temperature returns to normal and the state of health begins to improve. Then you can even make short walks.
Chickenpox is a simple disease and, with proper care, passes quickly and imperceptibly, but if there are some symptoms that have alerted the parents, the child should immediately be shown to the doctor. "
Prevention and vaccinations
The main prevention of the disease is timely vaccination of children. Such vaccinations appeared relatively recently, but have already shown their effectiveness. Those adults and children who have not had chickenpox, as determined by a blood test, are vaccinated.
Vaccinations can prevent the development of chickenpox even when there has been contact with an infected person, if done for 2 - 3 days immediately after direct contact.
Vaccinations also give pregnant women to protect the baby inside, because the virus affects both the mother and the child. Intrauterine infection of the child leads to serious consequences, starting with the defeat of the internal organs of the child and ending with miscarriage.
Infection is particularly dangerous in the last few days, so a vaccine should be vaccinated in time if the expectant mother has not yet suffered from this disease.

Vaccines against chickenpox do:
- from 12 months to 13 years - one injection;
- from 13 years old to the child - 2 injections with a break in 4 - 8 weeks;
- after contact with the patient - one injection in the first 48 hours.
Vaccinated is prohibited in cases where:
- are allergic to vaccine components: neomycin or gelatin;
- during exacerbation of chronic disease;
- during pregnancy;
- after a blood transfusion, if it was less than 3 months ago.
Can I get sick the second time?
There is a widespread belief that after a child has had chickenpox for the second time he cannot get sick. And this is indeed the case, 97% of all people who have been ill have lifelong immunity to chicken pox. And only the remaining 3% can fall ill again. Infants up to 6 months also have immunity to the virus, because their mother, who had been ill in childhood. She gave her antibodies through the placenta.
For more information about chicken pox in children, see the following video.