Dry coughing in adults can be a sign that warns a number of respiratory and non-respiratory diseases. Treatment is primarily based on the elimination of the main reasons that provoke its appearance.

Forms of dry cough and common causes
Acute or short-term form in the overwhelming majority of cases is caused by upper respiratory tract infections (catarrhal diseases) and is local in nature. As healing occurs, the airways clear up, and when the infection reaches its peak, the cough usually becomes productive.
Common causes of chronic dry cough in an adult are:
- Hay fever (or allergic rhinitis): a common allergic condition that mimics cold symptoms;
- Pollutants (atmospheric pollutants and exposure to passive smoking), irritating the back of the throat;

- Inhalation of irritants: the usual cascade of reactions to non-toxic or toxic gases and vapors also includes inflammation of the throat and respiratory tract;
- Postnasal syndrome: a condition in which mucus flows down the back of the nasopharynx into the larynx, irritating the cough receptors;
- Cough asthma is defined as a persistent non-productive cough with shortness of breath;
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Acid Reflux): A digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter, in which the contents of the stomach (a small amount of acid) are discharged into the upper respiratory tract, causing, in addition to cough, heartburn, burning in the throat or increased saliva, shortness of breath, pain chest
Chronic coughing remains a serious condition both physically and psychologically and sometimes leads to serious complications, including constant fatigue, sleep disturbance, stress urinary incontinence.
Differential diagnostics
Identifying the cause of cough usually begins with the determination of its specific or non-specific nature. A specific cough is associated with other symptoms, and further examination depends on them.
Nonspecific type occurs without visible signs and symptoms. Further examination may include laboratory analysis, x-rays and spirometry.

Spirometry
Less common causes of dry cough:
- Pulmonary artery thromboembolism (pulmonary embolism): a potentially life-threatening condition (sudden blockage in the pulmonary artery), among the common symptoms of which are dyspnea and unproductive cough;
- Pneumothorax (defined as the accumulation of air or gas in the pleural cavity). Most often observed in smokers with a history of pulmonary emphysema;
- Heart failure leads to fluid accumulation in the lungs and coughing attacks, especially during sleep;
- Whooping cough (or contagious bacterial infection of the lungs and respiratory tract) is characterized by a sharp, hacking cough, accompanied by a "whistling" sound;
- Tuberculosis: a highly infectious bacterial disease that primarily affects the lungs. In the early stages leads to persistent dry cough;
- Psychogenic cough: not caused by any disease, but the cough reflex becomes a habit. The man does not even realize that he is coughing.
In addition, dry cough is caused and aggravated by some drugs used in the treatment of high blood pressure (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors) and heart disease. But only a doctor is able to evaluate the symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment.
How long does the acute and chronic form last
People often underestimate how long a cough can last. It drags on for more than a week and often provokes a decision to turn to antibiotics. In reality, antibiotics do not help with viral diseases, moreover they lead to negative consequences, causing an imbalance in the microbiome of the body.
Excessive use of antibiotics contributes to the natural mutation of pathogenic bacteria and the creation of new, resistant strains.
- The average duration of cough, which is described as acute (short-term) and is associated with a cold or flu, is almost 18 days;

- Subacute or post-infectious cough may persist for several (3 to 8) weeks after the disease;
- A cough that lasts more than 8 weeks is chronic (persistent) persistent.
With seasonal changes, most people fall victim to a cold and it’s normal if the patient coughs 2 or even 3 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Seek medical attention in case of deterioration (high temperature, shortness of breath). In some cases, even nervous excitement and poor immunity can cause a cough that lasts for 2 weeks.
Features dry cough without temperature
Cough is a symptom. It is classified by duration and other typical features. The clinical picture is clear when a person has a cold or has contracted a viral respiratory disease: fever, runny nose, tearing, weakness, and other symptoms of intoxication characteristic of the disease.
In these cases, the reason is obvious. But dry cough without a temperature in adults for a long time, despite the seeming harmlessness, is a sign of a serious illness.
- Dry cough, along with chest tightness, wheezing, wheezing is a characteristic symptom of asthma, which is usually worse at night or in the early morning (uncontrolled symptom causes fecal or urinary incontinence, disrupts social activity);
- With an allergic reaction, signs such as nasal congestion and sneezing are observed;
- Cough with a tickling sensation in the back of the throat, aggravated at night, with post-nasal syndrome.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease affects the lungs and is the cause of subacute and chronic spasmodic coughing (the esophagus and the lung have a common embryonic onset and innervation of the vagus nerve);
- A cough associated with medications appears several weeks after the start of medication.
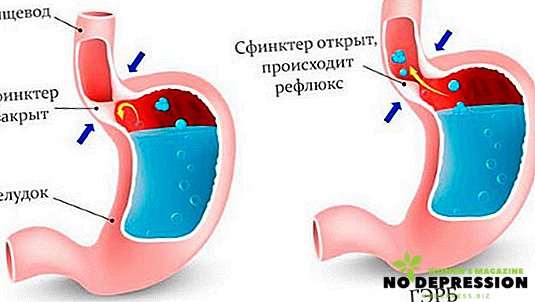
In pneumonia, it begins as dry, but after a while it goes into the wet type with the release of yellowish or greenish mucus. Accompanied by fever, chills, difficulty breathing, or chest pain when inhaled.
How to relieve a dry cough: pharmacology
The specific treatment of dry cough in adults depends on identifying the cause, which is able to control it, but this does not happen in all cases. When they cannot identify any cause, and coughing interferes with daily human activities, symptomatic relief should be considered.
- Dry type is treated with antitussive drugs, available in combination with antihistamine drugs, decongestants and expectorant drugs;
- Expectorant (acetylcysteine and guaifenesin): allegedly alleviate the condition, increasing the production of mucus and sputum;
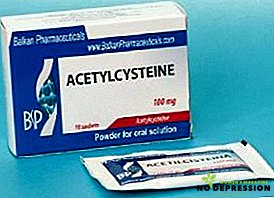
- Antitussives (codeine, folkcodine, dextromethorphan, noscapine butamiraty; stronger opiates: morphine, diamorphine and methadone): they suppress the problem, they can regenerate the mucous membrane, although the effect will be less if lung irritation continues;
- Antihistamines (chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine): cause a moderate sedative effect and reduce other associated symptoms (runny nose and watery eyes);
- Decongestants (phenylephrine, pseudoephedrine, ephedrine, oxymetazoline, or xylometazoline) make it easier with nasal congestion.
In effective doses, the antitussive drugs have side effects, such as drowsiness, nausea, constipation, and physical dependence. In high doses, they even depress the respiratory center.
Folk remedies in the treatment
A wide variety of herbal medicines possesset antiviral, expectorant and immunoprovelable action related to the treatment of dry cough. Recommended steam inhalation with medicinal decoction, helping to moisturize the airways, reduce inflammation and irritation of the throat.
Methods of treatment of folk remedies at home:
- The most effective tool with expectorant action is decoction of elecampane. 25 g of crushed rhizomes pour 1 cup of water and cook for 10 minutes. Infuse the mixture for 4 hours. Drink 25 ml every 6 hours half an hour before meals;
- Infusion of cranberry marsh: 30 g of cranberry marsh leaves pour 300 ml of boiling water and infuse for 5-6 hours. Filter and drink 50 ml 3 times a day;
- An excellent expectorant is considered pine needle syrup. To prepare it, you need 100 g of crushed pine needles, which are poured with 500 ml of boiling water and allowed to stand for 3 hours. Then the broth is boiled over low heat for 2 minutes, filtered, add 250-300 grams of sugar and boil until thick. Take 25-30 ml 3 times a day after meals;
- In the treatment of honey is widely used, both in pure form and for the preparation of various means.

Only an integrated approach, including drug treatment, physiotherapy and traditional medicine, helps to reduce inflammation and normalize organs, preventing the development of complications and chronic forms of the disease.
Hot and choking cough: causes and treatment
Dry paroxysmal cough, painful and debilitating, is a symptom of some forms of inflammation and allergic reactions of the respiratory system. Spasms of the respiratory tract can lead to vomiting, provoke ruptures of small blood vessels and damage the mucous membrane.
Observed:
- in people with diagnosed allergies to flowering, dust, mites, animal dander;
- in patients with bronchial asthma;
- in patients with allergies in the family history.
The respiratory system of people suffering from skin allergies is extremely sensitive to the effects of toxic and irritating substances. To determine the list of allergens and eliminate the symptom, first of all, you need to pass a blood test or skin tests for allergies.

How to treat a dry paroxysmal and choking cough in an adult? Treatment involves treating the main symptoms with antihistamines, also to prevent relapses.
If the patient's condition worsens, it may be necessary to use a nebulizer: inhalation makes it easier for the patient to breathe by expanding the bronchioles.
Acute and chronic complications
Complications seem to be related to physiological processes. The force of pressure and energy that occurs when a strong cough, allows him to be an effective means of cleaning the respiratory tract from excessive secretion and foreign material and ensure cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
However, it also causes many deep physical and psychosocial complications. Negative consequences include cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, neurological, ophthalmic, psychosocial, respiratory and skin complications, reduced quality of life associated with health.
Complications can be classified as acute or chronic. Acute complications include fainting cough (fainting due to reduced blood flow to the brain with prolonged and severe cough), insomnia, vomiting, rupture of air bubbles causing spontaneous pneumothorax, subconjunctival bleeding, hemorrhoids.

Chronic complications are common and include abdominal or pelvic hernia, fatigue fractures of the lower ribs and rib dystrophy. Determining the cause of chronic cough is crucial for effective treatment.
Reviews
I am worried about bronchitis at least twice a year. The cough is so strong that the abdominal muscles hurt. The only thing that relieves my suffering is syrup with codeine. I believe that codeine, available in the form of tablets, syrup, in combination with antipyretic drugs (paracetamol), is not only one of the most commonly used antitussive drugs in clinical practice. It should still be considered as a standard cough suppressant, for which new medicines are being evaluated.
Marina, 34, Moscow
All cough syrups containing sweeteners (sucrose, glucose, honey, or molasses) work precisely because of their sweet taste. The main focus of these drugs is the effect on placebo, not the pharmacological effect of the active ingredient. When a cough occurs, I try to heal with folk remedies, I drink teas brewed on medicinal herbs. I eat chocolate. The fact is that the theobromine contained in the product suppresses the activity of the vagus nerve, which causes coughing, and stops coughing more effectively than codeine.
Olga, 40 years old, Vladivostok
In the following video, there is some more additional information about the treatment of dry cough in adults.