Rubella is an acute viral disease that is most common in children under 9 years of age. In our material we will study the symptoms of this disease, its danger, possible complications and methods of treatment. And also tell you what the virus is dangerous for pregnant women.
Characteristics of the pathogen, methods of transmission
Rubella is an infectious disease, and in humans, the susceptibility to it is over 90%. The causative agent is Rubella virus. Getting into the external environment, dies after 5-8 hours. Moreover, it quickly dies when exposed to sunlight, high temperature, and is afraid of various disinfectants. But at the same time it quietly tolerates low temperatures - it can remain active for several years when frozen.
Most rubella sick in the offseason. Transmission occurs from a person infected with the virus in three ways:
- Airborne, for example when kissing, sneezing.
- Contact - through the dishes, other household items.
- Transplacental, that is, from a pregnant woman to a child.
 In the first and second cases, it is possible to talk about acquired rubella, when exactly the mucous membranes of the mouth and respiratory tract are the “entrance gate”. After that, the virus enters the bloodstream and quickly spreads to all organs. The incubation period is about three weeks. But if the virus is transmitted from mother to child, rubella is considered congenital.
In the first and second cases, it is possible to talk about acquired rubella, when exactly the mucous membranes of the mouth and respiratory tract are the “entrance gate”. After that, the virus enters the bloodstream and quickly spreads to all organs. The incubation period is about three weeks. But if the virus is transmitted from mother to child, rubella is considered congenital.
The carrier of the virus is particularly dangerous in the second half of the incubation period, that is, 7-10 days before and after the rash. As quickly as possible, it spreads in closed rooms and in places where large numbers of people gather.
But then, after suffering the disease, a person forms an immunity to the virus, and recurrent disease happens very rarely (with severe disruptions of the immune system).
Main symptoms of rubella in children
The first symptoms usually appear at the very end of the incubation period, and he usually proceeds with absolutely no signs: some complain of indisposition, weakness, drowsiness.
At this stage, the main signs of rubella can be called a small increase in lymph nodes: first in the groin, then in the armpits, after the ears.
Moreover, it is worth noting that the lymph nodes on the back of the head are the most unstable to rubella - this is where the virus usually multiplies.
Also, this disease happens prodromal period, which lasts from two hours to two days. Characterized by symptoms such as:
- muscle pain;
- lack of appetite;
- headache;
- weakness;
- sore throat;
- stuffy nose
After several days, sharp pains in the neck begin to appear, lymph nodes swell up to 1 cm. In addition, symptoms such as:
- dry cough;
- elevated temperature;
- nasal congestion.
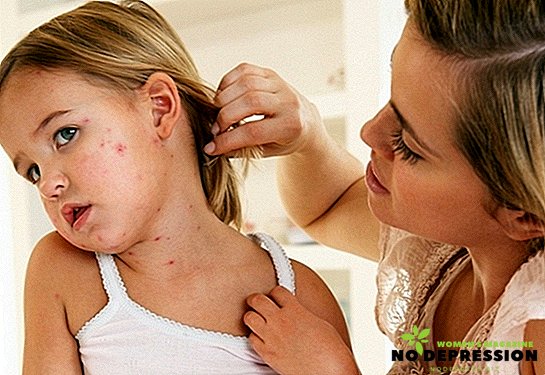
After a few more days, a reddish rash appears - the spots reach a diameter of 5 mm and do not merge with each other. The emergence of such a rash due to the effect of the virus on the capillaries that are under the skin. In just a couple of hours, a rash covers the entire body, except for the palms. After three days, the spots turn into nodules, gradually turn pale and disappear - the scars do not remain after them.
The rash can remain on the body for up to a week, after which the patient's condition begins to gradually improve: appetite comes, cough disappears, breathing becomes even, and runny nose disappears. Lymph nodes return to their return state after a maximum of three weeks.
Rubella forms
In children, rubella can be of two types:
- Atypical.
- Typical.
If the rubella is of a typical form, then there is a clinical picture, which we mentioned above, but with an atypical form, there may be no rash and a number of other symptoms. Because of this, such rubella is more dangerous from the point of view of the inability to control the release of the virus.
How is the diagnosis
 Primary diagnosis is as follows:
Primary diagnosis is as follows:
- First, a survey is conducted.
- The child is sent for testing.
- A general examination of the mucous and lymph nodes.
The child needs to be tested for blood and urine, and if the urine does not show anything, then the number of lymphocytes in the blood will be increased, possibly an ESR. In the absence of a rash, a special assay can be administered that will show the presence of antibodies to this virus. Moreover, such a test is better to take two times: in the first days after the onset of symptoms and a week later.
Differences from other diseases
In the atypical form of this disease, the symptoms are mild, therefore rubella is often confused with other diseases. That is why it is so important to learn to distinguish between them. Often, external signs are similar to diseases such as mononucleosis, scarlet fever.
For example, in contrast to measles, this disease is usually not accompanied by high fever, a rash that does not connect with each other, moreover, there is no change on the mucous membrane.
The difference from scarlet fever is that there is no blanching of the skin between the nose and lip, the rash is larger in diameter, often appears on the back, but not on the chest, not on the folds of the arms.
Unlike a disease such as mononucleosis, with rubella there is no purulent tonsillitis, the liver and spleen are not enlarged.
Treatment recommendations
This disease in children proceeds quite easily and with almost no complications, the only exception is a disease of congenital form, infants or children with severe pathologies can be hospitalized.
There is no specific treatment for this disease. Doctors simply recommend:
- Observe bed rest during the week.
- To carry out wet cleaning, often ventilate the room.
- Give your baby a lot of drinking.
- There are small portions, and the dishes should be dietary.
 Among the drugs you need to choose those that will help relieve the symptoms associated with rubella. For example, it may be vitamins, with a serious rash prescribed antihistamines (for example, Suprastin), at a temperature of more than +38 degrees usually prescribed antipyretic agents.
Among the drugs you need to choose those that will help relieve the symptoms associated with rubella. For example, it may be vitamins, with a serious rash prescribed antihistamines (for example, Suprastin), at a temperature of more than +38 degrees usually prescribed antipyretic agents.
With a sore throat, absorbable tablets (Lizobact) are prescribed, and with nasal congestion, vasoconstrictor drops are prescribed.
In the presence of a bacterial infection antibacterial drugs are used.
Rubella in children under 1 year
In children of this age, this disease is very rare. It’s pretty simple to explain: many women had either had rubella or had been vaccinated by the time their children were born. In this case, when breastfeeding from the mother to the child, antibodies to many infections are transmitted, so the baby is under reliable protection.
It is important to remember that the rubella in babies is very dangerous, since it is often accompanied by convulsions and can cause the development of meningitis. And the disease develops incredibly quickly. Typical rubella eruptions can appear in just a couple of hours and immediately disappear. Therefore, if you see anxiety, there are other signs of this disease, you should immediately call a doctor.
What can lead rubella in pregnant women
The most dangerous is intrauterine infection. And the later it happened, the more favorable the prognosis for recovery. For example, if a woman gets sick before 12 weeks, the likelihood of such consequences as:
- Death of the fetus, miscarriage.
- Abnormalities in the development of the child (CNS damage, defects in the development of bone tissue).
- Eye damage and possible blindness.
- Deviations in the work of the heart and blood vessels, such as heart disease
 The main danger is that this virus inhibits the development and division of cells, with the result that some organs may stop growing.
The main danger is that this virus inhibits the development and division of cells, with the result that some organs may stop growing.
In addition, rubella can lead to fetal ischemia due to vascular lesions of the placenta, and the virus suppresses fetal immunity.
After 14 weeks of pregnancy, the risks of complications are not so serious, but they are still present: the development of mental disorders is possible, a delay in the development of the fetus.
The main signs of this include low birth weight of the child, inadequate reaction to external stimuli.
Complications and Prevention
With a weak immunity, rubella can lead to a number of complications (and most often they occur against the background of bacterial infections). The most common complications include:
- Angina.
- Bronchitis.
- Encephalitis.
It is also possible complications in the form of otitis media and even mikardita.
And in order to never encounter such a disease as rubella, it is desirable to vaccinate, which is carried out according to this scheme:
- The first time they make a vaccine at the age of about a year.
- The last time - in 6 years.
After that, the baby will be resistant immunity to rubella. But there are also several other important recommendations that will help avoid many childhood infections and illnesses:
- Isolation of the patient in a separate room.
- Personal hygiene.
- Provision of individual household items, such as dishes, towels.
- Conducting wet cleaning, airing in the room.
These simple tips will help you to avoid infecting other relatives.